OUTLINE:
Step Down Transformer: Principle of Operation and Wide Range of Applications
 451
451With the advancement of technology and the increasing demand for electricity in both industrial and residential settings, the need for electrical transformers has risen. One such transformer widely used is the step-down transformer, which can lower the voltage of an electrical current and enable efficient and safe transmission and usage of electricity in power distribution systems.
What is a step down transformer?
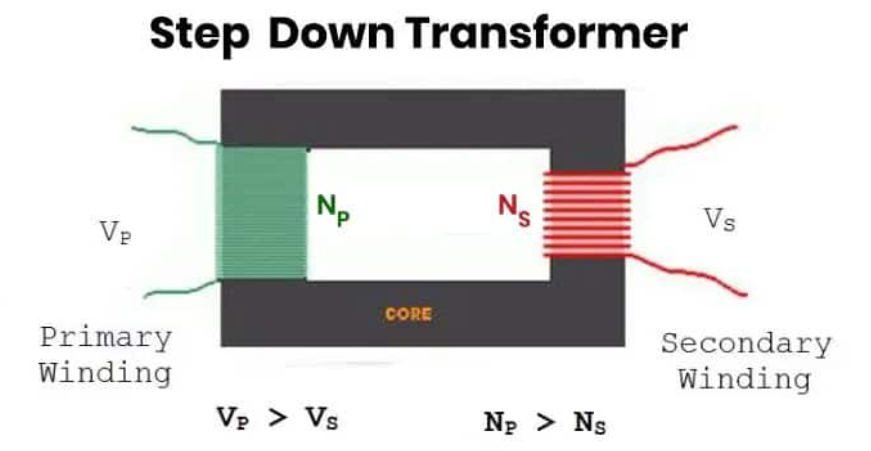
With the advancements in technology and the growing demand for electricity in both industrial and residential settings, the need for electrical transformers has increased. A step-down transformer is one such transformer that is used to lower the voltage of an electrical current. It works by having fewer turns in the secondary coil than in the primary coil, resulting in a decrease in voltage. This makes it an essential component of the power distribution system, allowing for efficient transmission and safe usage of electricity.
How do step down transformer work?
Step-down transformers work on the principle of electromagnetic induction. They consist of two coils, the primary and secondary winding, that share a magnetic field and have a high level of mutual induction. When an alternating current (AC) passes through the primary winding, it produces a varying magnetic field that induces an AC voltage in the secondary winding.
A step-down transformer is used when the voltage needs to be reduced from a high level to a lower level. This is important because high voltage can be dangerous both for machines and human safety. High voltage can cause electric shocks, fires, or even explosions if not handled properly. Therefore, step-down transformers are used to reduce the voltage to a safe level before it is used in homes and industries.
For example, the voltage generated by power plants can be very high, typically between 110 kV to 765 kV, which is not safe for domestic or commercial use. Therefore, step-down transformers are used to lower the voltage to a level that is safe for use in homes and industries, typically between 110 V to 220 V. This makes it possible to distribute electricity safely and efficiently, while also protecting equipment and people from the dangers of high voltage.
What is the differences between a step up transformer vs a step down transformer?
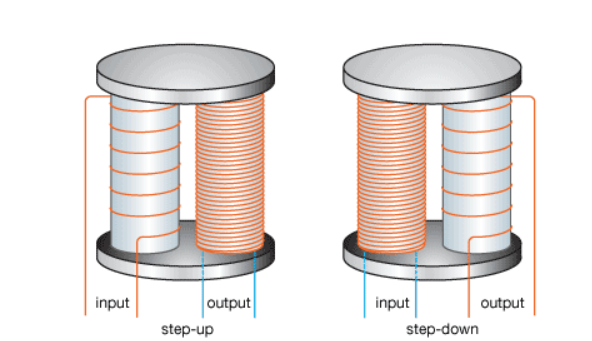
The main difference between a step-up transformer and a step-down transformer is their purpose. A step-up transformer is designed to increase the voltage from a low level to a higher level, while a step-down transformer is designed to decrease the voltage from a higher level to a lower level.
The construction of both transformers is similar, consisting of two coils, the primary and secondary windings, that share a magnetic field and have a high level of mutual induction. However, the number of turns in the primary and secondary coils is different. In a step-up transformer, the number of turns in the secondary coil is greater than the number of turns in the primary coil, while in a step-down transformer, the number of turns in the primary coil is greater than the number of turns in the secondary coil.
What are the applications of step down transformers?
Step-down transformers are used in power adaptors and rectifiers to efficiently decrease the voltage.
Main adapters
Cell phone chargers
Stereos
CD players

Other applications include:
Power transmission lines
Welding machines
Voltage stabilizers and inverters
It is evident that the step-down transformer plays a crucial role in the power system. Understanding how a step-down transformer works and its significance in making electricity safe for use in homes is crucial for ensuring the safety and reliability of the power system.

Disclaimer: The views and opinions expressed by individual authors or forum participants on this website do not represent the views and opinions of Chipsmall, nor do they represent Chipsmall's official policy.

share this blog to:

