OUTLINE:
Basic Knowledge of BC547 Transistor
 283
283Prepare to embark on an enlightening journey through the intricate world of electronics as we unveil the inner workings of the BC547 transistor.
In this comprehensive guide, we delve deep into its core, illuminating fundamental principles and unveiling practical applications.
From its inception to its contemporary relevance, join us as we navigate the labyrinth of circuitry, equipping you with the essential knowledge to harness the power of this versatile component with confidence and finesse.

Image source:Amazon.com
What Is A BC547 Transistor
The BC547 is a type of bipolar junction transistor (BJT) commonly used in electronic circuits.
Specifically, it is an NPN (negative-positive-negative) transistor, meaning it consists of three semiconductor layers: a thin layer of P-doped semiconductor (the "base") sandwiched between two thicker layers of N-doped semiconductor (the "emitter" and "collector").
Functionally, the BC547 transistor acts as an amplifier or a switch in electronic circuits.
When used as an amplifier, small variations in the current or voltage applied to the base terminal can control much larger currents flowing between the collector and emitter terminals.
This property makes it useful in audio amplification, signal processing, and other applications where amplification is necessary.
As a switch, the BC547 transistor can control the flow of current between the collector and emitter terminals by varying the current applied to the base terminal.
This allows it to function as an on/off switch in digital circuits, enabling tasks such as turning on or off LEDs, driving motors, or controlling other electronic components.
What Are the Applications of BC547 Transistor
The BC547 transistor finds application in various electronic circuits due to its versatility and reliability. Some common applications include:
Amplification: BC547 transistors are frequently used as small-signal amplifiers in audio circuits, such as microphone preamplifiers, headphone amplifiers, and low-power audio amplifiers. They can also amplify weak signals in radio frequency (RF) circuits.
Switching: These transistors are employed as switches in digital circuits. By controlling the base current, the BC547 transistor can turn on or off larger currents flowing through other components, such as LEDs, relays, or motors. This makes them suitable for use in logic gates, digital controllers, and power switching circuits.
Oscillation: BC547 transistors are utilized in oscillator circuits to generate periodic signals, such as square waves, sine waves, or pulse waves. These oscillators are crucial components in applications like clock generators, frequency synthesizers, and tone generators for musical instruments.
Signal Processing: They play a role in signal processing circuits, such as filters, modulators, and demodulators. BC547 transistors can manipulate and process signals to extract useful information or perform specific functions, like frequency filtering or amplitude modulation/demodulation.
Voltage Regulation: In voltage regulation circuits, BC547 transistors can be part of voltage regulators or voltage references. They help stabilize and regulate the output voltage, ensuring a consistent and reliable power supply for other components in the circuit.
Sensor Interfaces: BC547 transistors are used in sensor interface circuits to amplify and condition weak signals from sensors, such as temperature sensors, light sensors, or pressure sensors. They help convert these signals into a usable form for further processing or analysis.
The Two Operational Status of BC547 Transistor
The BC547 transistor operates in different modes based on the biasing of its junctions, specifically the base-emitter junction (Junction 1) and the collector-base junction (Junction 2). These modes are commonly referred to as:
- Active Region (Forward-Active Mode): In this state, the BC547 transistor operates as an amplifier. A small current flows into the base terminal (IB), which controls a much larger current flowing between the collector and emitter terminals (IC). The transistor is biased such that it is in forward-active mode, allowing it to amplify signals. In this region, both the collector-base junction (Junction 1) and the base-emitter junction (Junction 2) are forward-biased. The transistor exhibits high current gain (β), making it suitable for amplification purposes.
- Cutoff Region: When there is no base current (IB = 0), the transistor is in the cutoff region. In this state, both junctions of the transistor are reverse-biased. As a result, no significant current flows between the collector and emitter terminals (IC ≈ 0). The transistor essentially acts as an open circuit, blocking the flow of current. This state is analogous to an "off" switch in digital applications, where the transistor effectively interrupts the flow of current through the circuit.
Is BC547 Transistor PNP or NPN
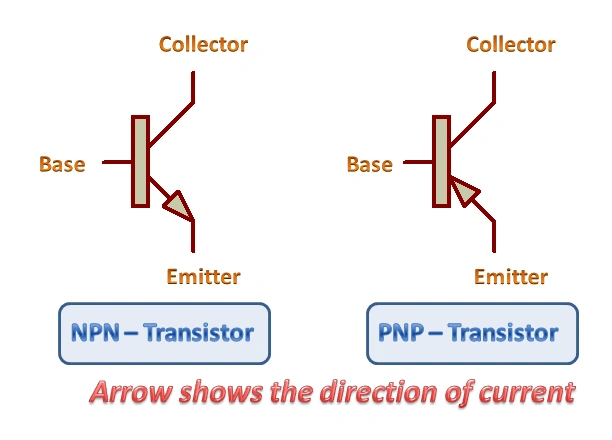
The BC547 transistor is an NPN (Negative-Positive-Negative) bipolar junction transistor (BJT).
In an NPN transistor like the BC547, there are two layers of N-type semiconductor material surrounding a layer of P-type semiconductor material.
In an NPN transistor, current flows from the collector (which is N-type) to the emitter (which is also N-type) when a small current is applied to the base (which is P-type).
This makes the BC547 transistor suitable for a wide range of applications, including amplification and switching in electronic circuits.
Can BC547 Transistor Handle 12v
The answer is:Yes, the BC547 transistor can typically handle a 12V supply voltage.
The BC547 transistor is typically rated for a maximum collector-emitter voltage (VCEO) of around 45 volts.
However, it's essential to consider the specific datasheet of the BC547 transistor you're using, as there might be variations between manufacturers or specific models.
If you intend to use the BC547 transistor in a circuit with a 12V supply voltage, it should generally be able to handle it without issues, assuming that the voltage across the collector-emitter junction does not exceed its maximum rating.
Ensure that the collector-emitter voltage (VCE) in your circuit remains well within the specified limits to prevent damaging the transistor.
Additionally, consider other factors such as the current passing through the transistor (collector current, IC) and power dissipation to ensure the transistor operates within its safe operating limits.
Always refer to the transistor's datasheet for precise specifications and guidelines regarding voltage, current, and power ratings to ensure safe and reliable operation in your circuit.
Final Verdict
Gaining a foundational understanding of the BC547 transistor unlocks a realm of possibilities in electronics.
By delving into its fundamentals and applications, we've illuminated its role as a versatile component in circuits, capable of amplification, switching, and signal processing tasks.
Armed with this basic knowledge, you're well-equipped to explore further and harness the potential of the BC547 transistor in your own electronic projects and endeavors.

Disclaimer: The views and opinions expressed by individual authors or forum participants on this website do not represent the views and opinions of Chipsmall, nor do they represent Chipsmall's official policy.

share this blog to:






