OUTLINE:
Brake Booster Replacement Cost: You Need to Know Before You Hit the Brakes
 142
142Hey, when it comes to maintaining our car, the brake booster is really a big deal. It's related to whether the brakes work properly and whether it's safe or not. But if there is a problem with it, how much will it cost to replace it with a new one?

Image Source: Autonation Mobile Service
This matter will become complicated, and we need to pay attention to several aspects. Now let's talk about the things that determine the brake booster replacement cost , such as what model your car is, the mechanic's labor costs, and whether the parts are new or not. Whether you are in a hurry to change or want to prepare in advance, knowing these costs will give you a clear idea and make a wise choice to keep our car running smoothly.
When Should you Replace your Brake Booster
Knowing when to swap out your brake booster is key to keeping your car safe and running smoothly. Here are some telltale signs that it might be time for a new one:
Stiff Brake Pedal: If you find it really tough to push down your brake pedal, especially when the engine's off, your brake booster might be on its way out. The booster helps you brake by using vacuum pressure, and if that's gone, braking gets harder.
Longer Stops: A brake booster that's not working right can make it take longer to stop your car. If you have to push harder on the brake to slow down, get that booster checked.
Hissing Sounds: If you hear a hissing noise near the brake pedal when you press it, that could mean there's a vacuum leak in the booster. It's a clear sign of wear and tear that might mean you need a new one.
Soft or Slow Brake Pedal: If your brake pedal feels like it's giving in or not doing much, there might be a problem with the booster or another part of the braking system. A booster that's not working right can mess up how your brakes feel.
Warning Lights: Some newer cars have a brake system warning light that turns on if there's an issue with the brake booster. Check your car's manual to see if there are any specific warning signs related to brake problems.
Trouble Starting: Since the brake booster needs the engine's vacuum to work right, problems with it can sometimes mess up the engine too. If you're having trouble starting your car or notice a drop in performance, it might be connected to the brake booster.
List of Brake Booster Replacement in 2024
Image Source: Repairpal.com
Here’s a comprehensive list of brake booster replacement options in 2024, along with insights into the brake booster replacement cost to help you make an informed choice:
1. OEM Brake Boosters
Made by your car's original manufacturer for a perfect fit.
Costs between 300and700 (not including labor).
Great for keeping that factory-fresh performance but costs a bit more.
2. Aftermarket Brake Boosters
Made by other companies to save you money.
Costs around 100 to 400.
A good budget choice, but quality can vary.
3. Remanufactured Brake Boosters
Fixed up and tested old parts.
Costs between 150 and 500.
Eco-friendly and balances price with quality.
4. Electric Brake Boosters
Found in newer hybrid or electric cars.
Costs 500to1,000 or more.
Expensive because of new tech and limited supply.
5. Vacuum-Assisted Brake Boosters
The old-school way, using your engine's vacuum.
Costs between 200 and 600.
Common and reliable in most regular cars.
6. Hydro-Boost Brake Boosters
Uses hydraulic pressure for heavy-duty braking.
Costs between 300 and 700.
Often used in trucks and SUVs for extra stopping power.
7. DIY Replacement Kits
For car lovers who want to save on labor.
Costs 100 to 300 (just for the parts).
Needs some tech skills and the right tools to install safely.
8. High-Performance Brake Boosters
Built for sports cars or custom setups that need top-notch braking.
Costs between 600and1,200.
Unmatched performance but at a higher price.
The Cost for Brake Booster Replacement
Replacing a brake booster is essential when this critical component fails, but the brake booster replacement cost can vary significantly depending on the vehicle, part type, and labor involved. Here's an in-depth look at typical costs, with examples for different scenarios:
1. Compact Cars
Example: Toyota Corolla
Cost: $250–$400
Compact cars usually have lower parts and labor costs, making them more affordable for repairs.
2. Sedans
Example: Honda Accord
Cost: $300–$600
Popular mid-size sedans often fall in the middle range for brake booster replacement cost due to part availability and moderate labor requirements.
3. SUVs
Example: Ford Explorer
Cost: $400–$800
Larger vehicles like SUVs often use more robust brake systems, increasing the price of replacement parts and labor.
4. Trucks
Example: Chevrolet Silverado
Cost: $500–$900
Trucks may require specialized hydro-boost systems, which typically come with a higher brake
booster replacement cost.
5. Luxury Vehicles
Example: BMW 5 Series
Cost: $700–$1,200
Luxury cars demand premium parts and often involve more labor, driving up replacement costs significantly.
6. Hybrid/Electric Vehicles
Example: Toyota Prius
Cost: $800–$1,500
Electric brake boosters used in hybrids or EVs are advanced and more expensive due to their specialized design.
What Factors Influence the Cost of Replacing a Brake Booster
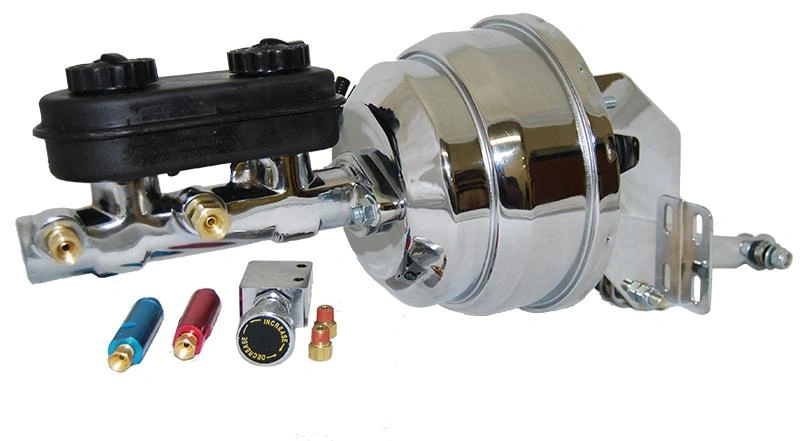

Image Source: Car From Japan.com
The brake booster replacement cost can vary significantly based on several key factors. Understanding these elements will help you anticipate the expenses involved and make informed decisions about repairs.
1. What Kind of Car You Have
Luxury or rare cars usually cost more because their brake systems are more complicated and parts are harder to find.
For example, fixing a brake booster in a BMW or Mercedes might be a lot pricier than in a Toyota or Ford.
2. Type of Brake Booster
Vacuum-Assisted: These are common and cheaper, usually costing 200to600 for parts.
Hydro-Boost: Found in trucks and SUVs, prices range from 300to700.
Electric: Used in hybrids and electrics, often costs 500to1,500 because of the new tech.
3. Labor Costs
Labor prices differ by place and repair shop, adding 150to300 or more to the total bill.
If your brake booster is hard to get to, it'll take longer and cost more.
4. Quality of Parts
OEM Parts: Perfect fit and performance but pricey, around 300to700.
Aftermarket Parts: Cheaper alternatives, usually 100to400, but quality can be different.
Remanufactured Parts: Eco-friendly and affordable, about 150to500.
5. Age and Condition of Your Car
Older cars might have harder-to-find parts, raising costs.
Rust or wear on nearby parts might need fixing too.
6. Where You Get the Work Done
Costs are often higher in cities because labor rates are up.
Dealerships usually cost more than independent shops for repairs.
7. Other Repairs Needed
A bad brake booster can mess up other parts like the master cylinder or vacuum pump, adding extra costs.
8. Availability of Parts
If your car is uncommon or old, parts might be hard to find, causing delays or higher prices.
Is DIY Brake Booster Replacement an Option to Cut Costs
Yes, DIY brake booster replacement can be an option to cut costs, but it comes with challenges and risks that need to be carefully considered. By replacing the brake booster yourself, you can save on labor costs, which typically range from $150 to $300, leaving you to pay only for the part, which can cost $100 to $300 depending on the type and quality.
However, the process is complex and requires advanced mechanical skills and specialized tools. Replacing a brake booster often involves disconnecting the brake system, removing components to access the booster, and ensuring everything is correctly reassembled. Mistakes during this process could lead to brake failure or other safety issues, making it a risky undertaking for those without significant experience.
If you're confident in your mechanical expertise and have access to the necessary tools, DIY replacement can be a cost-effective solution. For most vehicle owners, though, it's recommended to have the job done by a professional to ensure safety and proper functionality.
Final Verdict
Understanding the factors that influence brake booster replacement cost—such as vehicle type, part quality, and labor rates—can help you make informed decisions. Whether you opt for OEM, aftermarket, or remanufactured parts, prioritizing safety and quality ensures your braking system remains reliable and effective.

Disclaimer: The views and opinions expressed by individual authors or forum participants on this website do not represent the views and opinions of Chipsmall, nor do they represent Chipsmall's official policy.

share this blog to:

