OUTLINE:
The Ultimate Guide to Different Types of IC
 439
439Integrated Circuits (ICs) are the cornerstone of modern electronics. They are the heart and brain of most circuits. They are ubiquitous and you can find them on almost every circuit board. Therefore, it is very important to know and understand these chips.
The chip is the smallest unit of the application circuit. Because the chip is too small to be soldered or connected. In order to make the work of connecting the circuit to the chip easier, chip packaging technology is needed.
In this article, we will have detailed explanations of various IC types and different types of IC packages.

Image Source: MOKO Technology
How to Classify Integrated Circuit
Integrated circuits can be classified into many different types according to their functions, structures, manufacturing processes and other characteristics. The following are some common integrated circuit classifications
Functions
It can be divided into 3 categories according to their functions: analog integrated circuits, digital integrated circuits, mixed-signal integrated circuits.
1. Analog integrated circuit: It refers to an integrated circuit that is composed of analog circuits composed of capacitors, resistors, transistors, etc. and is used to process analog signals. Specific electronic components include: amplifiers, power management chips, analog multipliers. Analog ICs are generally composed of amplifiers, filters, feedback circuits, reference source circuits, and switched capacitor circuits.
Analog ICs are used to process continuous natural analog signals such as light, sound, speed, and temperature. Since there is broad room for domestic substitution of analog ICs, the demand for jobs in China is constantly expanding.
2. Digital integrated circuit: It is used to transmit, process and handle digital signals. It has been the fastest growing and most widely used in recent years. As a result, the demand for digital IC jobs has been rising in recent years.
Digital integrated circuits are small, with billions of logic gates, flip-flops, and multiplexers packed into just a few square millimeters. Their smaller size enables high-speed operation, minimal power dissipation, and cost-effective manufacture when compared to board-level integration. This category includes microprocessors, DSPs, and microcontrollers.
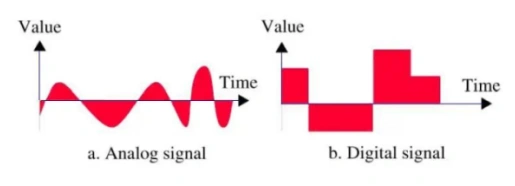
3. Mixed-signal integrated circuits: They combine analog and digital circuitry on a single chip, enabling operations such as analog-to-digital and digital-to-analog converters. While delivering smaller sizes and reduced costs, they must handle signal interference issues.
Mixed-signal integrated circuits are frequently employed to transform analog signals to digital signals, which digital devices can then handle. Mixed-signal integrated circuits, for example, are critical components for FM tuners in digital goods such as media players that include digital amplifiers. A very basic ADC can digitize any analog signal, and mixed-signal integrated circuits are the smallest and most energy efficient of them.
Role
1. Memory Integrated Circuit: MICs store and retrieve data. They consist of random-access memory (RAM), read-only memory (ROM), and flash memory. Memory integrated circuits are commonly utilized in computers, mobile devices, and embedded systems to store both temporary and permanent data.
Memory ICs are used in conjunction with processors to store program data and keep it during arithmetic operations. Memory ICs are used in all processor-equipped devices and computers, including cell phones, tablet terminals, personal computers, and mainframes.
2. Microprocessors: Microprocessors are the most complex ICs. They are made up of billions of transistors that have been organized into thousands of discrete digital circuits, each of which performs a specialized logic function. A microprocessor is made up completely of synchronized logic circuits. A microprocessor typically contains a computer's central processing unit (CPU).
Image Source: Britannica
Manufacturing
According to Integrated circuits can be divided into three categories according to their manufacturing processes: semiconductor integrated circuits, membrane integrated circuits and hybrid integrated circuits.
1. Semiconductor Integrated Circuits: They are active components such as transistors, diodes, and passive components such as resistors and capacitors that are interconnected according to certain circuits and integrated on a single semiconductor chip to complete specific circuit or system functions.
2. Membrane Integrated Circuits: Passive elements, such as resistors and capacitors in the form of films, are embedded on an insulating substrate and connected internally. Integrated circuits are divided into Thin-Film Integrated Circuits and Thick-Film Integrated Circuits according to the thickness of the element film.
3. Mixed Integrated Circuits: These circuits, also known as hybrid ICs, combine additional active elements such as diodes and transistors onto film Integrated Circuits and connect them via external wiring. Integrated circuits can alternatively be classified as Silicon ICs or Compound ICs based on the substrate material.
Conductivity
There are two types of integrated circuits based on conductivity: bipolar and unipolar.
1. Bipolar integrated circuits: They have superb frequency characteristics, but they consume a lot of power and require a sophisticated manufacturing process. Most analog and digital integrated circuits, including TTL, ECL, HTL, LST-TL, and STTL, fall under this category.
2. Unipolar integrated circuits: They have a slow working speed, but a high input impedance, low power consumption, a simple manufacturing process, and are easy to integrate on a large scale. Its major product is MOS integrated circuits.
Degree of integration
According to the degree of integration, they can be divided into four categories: small-scale, medium-scale, large-scale and ultra-large-scale integrated circuits.
For, analog integrated circuits, due to the high process requirements and complex circuits,
The integration of less than 50 components is a small-scale integrated circuit;
The integration of 50 to 100 components is a medium-scale integrated circuit;
The integration of more than 100 components is a large-scale integrated circuit;
For digital integrated circuits,
The integration of 1 to 10 equivalent gate (chip) circuits or 10 to 100 components (chips) is a small-scale integrated circuit
The integration of 10 to 100 equivalent gate (chip) circuits or 100 to 1,000 components (chips) is a medium-scale integrated circuit
The integration of 102 to 104 equivalent gate (chip) circuits or 103 to 105 components (chips) is a large-scale integrated circuit
The integration of more than 104 equivalent gate (chip) circuits or more than 105 components (chips) is an ultra-large-scale integrated circuit.
Different Types of IC Packages
Packaging technology takes the finished chip and expands it into a structure that is easier to connect to other circuits. Each external connection on the chip is connected to a pad or pin on the package through a small piece of gold wire. The pin is the silver extruded terminal on the chip circuit, which goes on to connect to other parts of the circuit.
There are many different types of packages, each with unique dimensions, mounting type, and number of pins. Let's take a closer look at some of the main package categories.
SMT (Surface Mount Technology)
Surface mount technology (SMT) is a popular method for packing and mounting electronic components onto printed circuit boards (PCBs). Electronic components in surface mount packages have flat, short leads or are completely leadless, and they are soldered to pads on the PCB's surface. Typically, a wiring scheme that matches the chip on the PCB must be created ahead of time and soldered to it.
SMT installation is normally done with automated equipment.This design has numerous major advantages. For starters, it allows for greater component density, which makes it easier to create smaller and more compact electrical devices. Second, surface mount components are lighter and have shorter electrical lines, which helps to improve electrical performance.
DIP (Dual In-line Package)
Their rectangular design with two parallel rows of metal legs for through-hole attachment makes them easily recognizable. Many tiny and medium-sized integrated circuits choose to use DIP packages, which typically have no more than 100 pins. Their simplicity and ease of use made them ideal for hobbyists and early electrical gadgets. However, their greater footprint renders them unsuitable for the downsizing standards of current electronics.
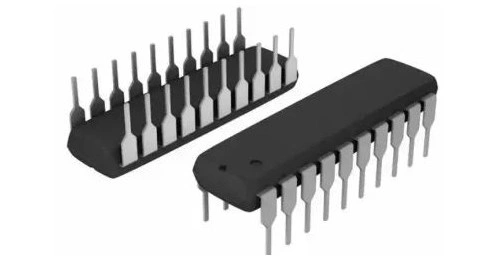
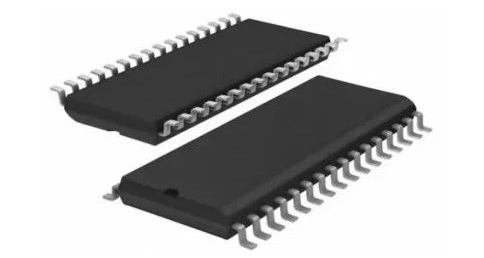
SOP (Small Outline Package)
As technology advanced and devices shrunk, so did the IC packages. SOPs offer a smaller footprint compared to DIPs, with leads extending from two sides of the package. SOP package has a wide range of applications and is one of the surface mount packages. It has gradually derived TSOP, SSOP, TSSOP, SOIC, etc., which have played a vital role in integrated circuits.
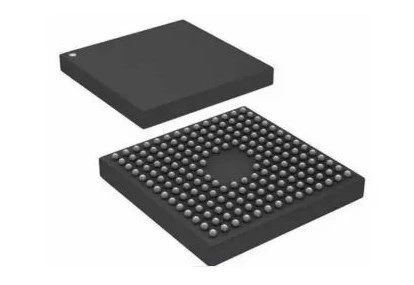
BGA (Ball Grid Array Package)
The terminals of the BGA package are distributed in an array under the package in the form of round or columnar solder joints. The advantage of BGA technology is that although the number of I/O pins has increased, the pin spacing has not decreased, but increased. However, this package is not convenient for manual welding and test measurement, and is mostly used in memory chips and other fields.
PLCC (Plastic Leaded Chip Carrier)
PLCC is a 32-pin package with a square shape and pins all around. Its dimensions are much smaller than those of DIP. PLCC is suitable for installation and wiring on PCBs using SMT surface mounting technology. It has the advantages of small dimensions and high reliability.
QFP (Quad Flat Package)
The leads are led out from four sides in an L-shape, the materials are ceramic, metal and plastic, among which, plastic packaging accounts for the vast majority.
The quad flat package process can effectively utilize space, thereby reducing the space requirements for printed circuit boards.
Depending on the thickness of the package body, QFP currently offers the following variations:
LQFP (Flat Quad Flat Pack): The height of the IC packaging body is 1.4 mm.
TQFP (Thin Quad Flat Pack): The height is 1.0mm.
PQFP (Plastic Quad Flat Package): This package features a small pitch and a very small pin. This IC packaging is typically used for large-scale or extremely large-scale integrated circuits, with a pin count of more than 100.
CQFP (Ceramic Quare Flat Package): The ceramic equivalent of PQFP.
BQFP (Quad Flat packaging with Bumper): This packaging features protrusions (cushions) at the four corners to avoid pin distortion during delivery.
IC Package Function
First of all, the purpose of packaging, in addition to protecting and supporting the chip itself, is to allow the chip to be connected to the external circuit through pins. Because after the chip is produced, it must be isolated from the outside world, otherwise the fine impurities in the air may corrode the fragile chip circuit, causing electrical performance degradation and direct damage;
And with the fixation of the package, the contact points on the chip can be connected to the pins of the package shell with wires, and these pins can be connected to other devices through the wires on the printed circuit board PCB, thereby realizing the connection between the internal chip and the external circuit.
Where to Buy Quality IC
Chipsmall Limited is made up of a professional staff with an average of more than 20 years' experience in electronic component distribution. With our vast global procurement channels and inventory reserves, we are confident in providing our customers with globally sourced, high-quality electronic components at a low cost and in the shortest amount of time.
We use "IDEA-STD-1010B" as our quality inspection standard and strictly adhere to AS9120, ESD, ISO9001, ISO14001, and other international standard systems, delivering only original and legitimate electronic components.
PMIC - Gate Drivers
PMIC - Voltage Regulators - Linear
Logic - Flip Flops
Logic - FIFOs Memory
Interface - Controllers
Interface - Specialized
Embedded - Microcontrollers
Embedded - FPGAs (Field Programmable Gate Array)
FAQ
What is the most common IC package
Dual Inline Package (DIP)
What's the distinction between an IC and a chip?
An integrated circuit (IC) is a microchip or computer chip. They are essentially the same thing. On an integrated circuit, transistors, resistors, capacitors, inductors, and other components and wiring are all coupled to form a circuit, hence the name. Computers and data storage devices use memory chips to store data and programs.
What is the most common type of IC?
The simplest and most common form of integrated circuit is logic ICs. They operate on binary signals using basic operations including AND, OR, NOT, NAND, NOR, XOR, and XNOR. Logic integrated circuits are divided into families based on their technology, speed, power consumption, and compatibility, including TTL, CMOS, ECL, and BiCMOS.

Disclaimer: The views and opinions expressed by individual authors or forum participants on this website do not represent the views and opinions of Chipsmall, nor do they represent Chipsmall's official policy.

share this blog to:











