OUTLINE:
A Guidance for Single Pole Double Throw (SPDT) Switch
 170
170Have you ever needed to switch between two circuits or control different signals without any hassle? That’s where a Single Pole Double Throw (SPDT) switch comes in.
.webp)
Image Source: Zhejiang Lierd Relay
This little gadget is a game-changer—it’s simple, flexible, and works in all kinds of projects, whether you’re building something cool at home or tackling a bigger setup. In this guide, we’ll break it all down—what an SPDT switch is, how it works, and why it’s so handy. Let’s jump in and see how this tiny tool can make your life easier!
Pre-view: What Is A Single Pole Double Throw Switch
Hey, you know what? That single pole double throw switch (let's call it SPDT switch) is just too convenient. You can easily switch between circuits with just a tap. It's like having a "head" (input) and two "hands" (output), you can pull this or that hand depending on your needs. Unlike ordinary switches, this SPDT small switch is much more flexible, not just simple to turn on or off.
Whether you are a DIY enthusiast who likes to do things by yourself or a curious friend about how circuits run, understanding this SPDT small switch will definitely make you feel "wow". Next, let's talk about how it is made, how it works, and how it can help. After we finish talking, you will surely understand why so much work cannot be done without this little guy. Come on, let's have a chat!
The Working Principle of A Single Pole Double Throw Switch
That single pole double throw switch is actually quite simple, but it has a wide range of uses. It can allow an input signal to switch between two different circuit paths, controlling the circuit.
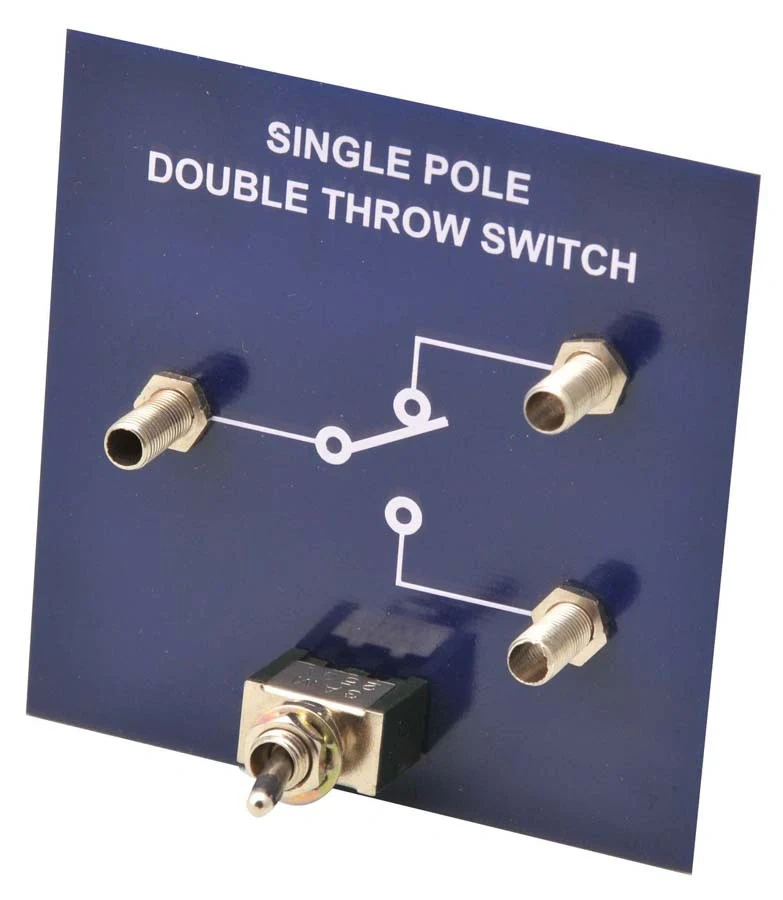

Image Source: Eisco Labs
Let's take a closer look at how it works:
Structural Overview
The SPDT small switch has three main connectors:
Head "(common connector): The place where current comes in.
Hand 1 "(first output connector): When the switch is in one position, this" hand "will be connected to another circuit or component.
Hand 2 "(second output connector): When the switch is in another position, this" hand "is connected to a different circuit or component.
Switch Action
When you toggle the switch (whether manual, mechanical, or electronic), the "head" will connect to either "hand 1" or "hand 2" based on the position of the switch.
Position 1: Connect the "head" to "hand 1", and the current will flow into the first circuit.
Position 2: Change the "head" to "hand 2", and the current will flow into the second circuit.
Working Principle
The "boss" receives an input signal or power supply, and the internal mechanism of the switch will either connect the "boss" to "hand 1" or "hand 2" according to its position.
At each position, there is always a 'hand' that completes the circuit connection, allowing current to flow to the connected devices or circuits.
Various Types of Single Pole Double Throw Switch
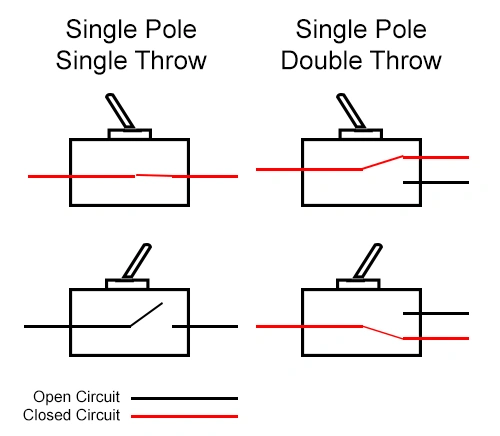
Image Source: CS-STEM Network
Single Pole Double Throw (SPDT) switches come in different types and designs based on their functionality, form, and method of operation. While the basic working principle remains the same, the way they are operated and their intended use can vary. Below are the main types of SPDT switches:
1. Toggle Switches
-
Description: Toggle switches are one of the most common types of SPDT switches. They have a lever that you flip up or down to switch between the two positions.
-
Applications: Often used in consumer electronics, light switches, and simple circuits where physical control is needed to change the connection.
-
Example: A light switch that toggles between two lighting circuits.
2. Pushbutton Switches
-
Description: Pushbutton SPDT switches are activated by pressing a button. Typically, they’re "momentary" switches, meaning they return to their default position once released.
-
Applications: Used in applications where you want the circuit to be active only while the button is pressed, such as in control panels, alarms, and certain motors.
-
Example: A doorbell switch or a "reset" button on an electronic device.
3. Slide Switches
-
Description: Slide switches have a small slider that moves back and forth to select between the two positions.
-
Applications: Common in small, portable devices like battery-powered gadgets, toys, and some electronic equipment where a low-profile, manual switch is needed.
-
Example: A switch used to control power between two different devices or battery banks in compact electronics.
4. Rotary Switches
-
Description: Rotary SPDT switches use a rotating dial or knob to select between the two positions. When turned, the switch moves between the positions to establish the electrical connection.
-
Applications: Used in situations where precise control or multiple options are needed, such as in radios, audio equipment, and motor controls.
-
Example: A volume control on a vintage radio that switches between two audio circuits.
5. Slide Lever Switches
-
Description: These are similar to slide switches, but they have a lever mechanism that slides across two terminals to toggle between the two outputs.
-
Applications: Typically used in small household appliances or on custom circuit boards where space is limited and a simple manual operation is required.
-
Example: A device that switches between two power sources or light settings in a small electronic gadget.
6. Miniature SPDT Switches
-
Description: These are compact, small-sized SPDT switches designed for use in tight spaces or on circuit boards where space is at a premium.
-
Applications: Common in electronic devices, toys, and small appliances, where a tiny and lightweight switch is needed for functionality.
-
Example: An SPDT switch in a camera that switches between modes or power sources.
7. Rotary Cam Switches
-
Description: A more complex form of rotary switch, a rotary cam switch has multiple positions but can also be wired as an SPDT switch to select between two outputs.
-
Applications: Typically used in industrial machinery, control panels, and advanced electronic systems requiring robust switching.
-
Example: A large control switch on industrial equipment where you need to alternate between two operational states.
8. Waterproof/SPDT Switches
-
Description: Waterproof or sealed SPDT switches are designed to be resistant to moisture, dust, and other environmental factors.
-
Applications: Common in outdoor or harsh environments like marine, automotive, and industrial equipment.
-
Example: A marine electrical switch used to alternate between power sources in a boat.
What Is the Difference between A Single and Double Pole Throw Switch
The main difference between a single pole switch and a double pole switch is how many circuits they can control.
Single pole single throw (we call it SPT small switch) is specifically used to control a circuit. It only has one input (we call it "boss") and one output, so it is particularly suitable for doing simple tasks such as turning on and off lights.
And the double knife switch (we call it DPT large switch) can handle two circuits at the same time. It has two inputs (two "heads") and two outputs, so it can switch between two circuits at once. This type of switch is particularly useful in more complex situations, such as when you need to simultaneously control the live and neutral wires in the system, or when you need to switch two poles at once when controlling a motor.
Is A Single Pole Double Throw Switch the same as A 3-way Switch
A Single Pole Double Throw (SPDT) switch and a 3-way switch are related, but they are not exactly the same. Here's how they differ:
An SPDT switch has one input terminal (the "pole") and two output terminals (the "throws"). It allows you to switch between two different circuits or outputs. When you flip the switch, the common pole connects to one of the throws, directing the current to that path. SPDT switches are often used in simpler circuits where you need to choose between two options.
A 3-way switch, commonly used in home lighting systems, is part of a pair of switches that control a single light from two different locations (like at the top and bottom of a staircase). It has three terminals: one common terminal (like the pole in an SPDT) and two traveler terminals. The traveler terminals connect to the other 3-way switch, which is why you need two of them for the system to work.
The key difference is that while both switches may appear to have multiple terminals (one input and two outputs), 3-way switches are specifically designed for controlling the same load from two locations, while SPDT switches are more general-purpose and used for switching between two circuits or paths in simpler applications.
Final Verdict
Understanding the Single Pole Double Throw (SPDT) switch is crucial for anyone working with electrical circuits, as it offers a versatile solution for controlling multiple paths or circuits. With its ability to switch between two different outputs using a single input, the SPDT switch plays a significant role in various applications, from simple devices to more complex systems. Whether you're using it for basic tasks like controlling lights or for more intricate setups like signal routing, the SPDT switch is a reliable and effective component in both household and industrial applications. By grasping its structure, working principle, and various types, you can confidently incorporate SPDT switches into your projects, ensuring flexibility and functionality in your electrical designs.

Disclaimer: The views and opinions expressed by individual authors or forum participants on this website do not represent the views and opinions of Chipsmall, nor do they represent Chipsmall's official policy.

share this blog to:











