OUTLINE:
Circuit Board Capacitor: All You Need to Know
 427
427Circuit board capacitors play a crucial role in the world of electronic devices, ensuring their proper functioning and performance. Their presence and right selection help to improve the performance, dependability, and lifetime of electronic systems.
What is a Circuit Board Capacitor
Capacitors are passive electronic components that store electrical energy by accumulating charges on insulated surfaces. They add capacitance to circuits and come in various forms. When a voltage is applied, charges collect on the capacitor plates, creating an electric field. Capacitors are widely used in electrical devices, power transmission systems, and digital computers for energy storage and voltage stabilization.
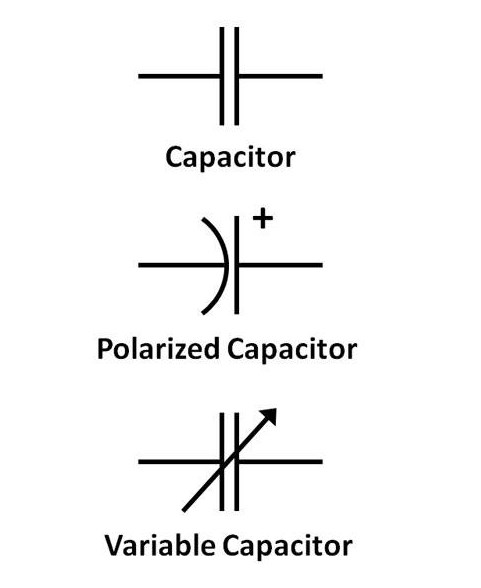
Capacitors Symbol in Circuit Board
There is a common way to represent a capacitor so that we can put it into schematics.
The capacitor polarity is represented by the '+' symbol on one of the capacitor pins, signifying that the greater voltage should be connected there.
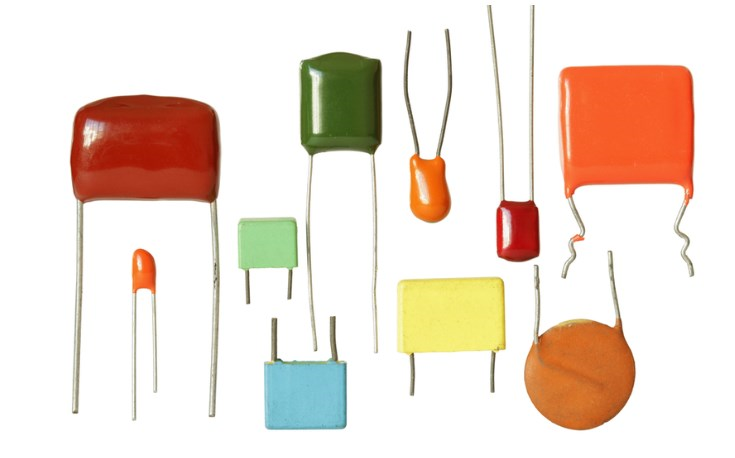
Types of Capacitors
Capacitors come in a variety of types, each with specific characteristics and applications.
- Ceramic Capacitors: Composed of ceramic materials, these capacitors are non-polarized. They are perfect for surface-mount technology (SMT) and high-frequency applications because they provide large capacitance values in compact packages. They have a wide range of values, from picofarads to microfarads, and are known for their stability and low cost.
- Electrolytic Capacitors: High capacitance polarized capacitors, usually used for decoupling and filtering power supplies. They are made up of a cathode, an electrolyte, and an anode made of tantalum or aluminum. Because they are polarity sensitive and have a short lifespan, electrolytics must be placed carefully on a circuit board.
- Tantalum Capacitors: Made of tantalum, these capacitors are similar to electrolytics in that they provide high capacitance in a compact form factor. They are appropriate for crucial applications since they are polarized and able to withstand high temperatures. When compared to aluminum electrolytics, they are less costly and have a lower voltage rating.
- Film Capacitors: Non-polarized capacitors that use a thin plastic film as the dielectric. Their stability throughout a broad temperature range, great accuracy, and low inductance are well recognized. Precision circuits, power supply, and audio equipment all employ film capacitors.
- Supercapacitors (Ultracapacitors): The high-capacity capacitors have a greater energy storage capacity per unit space than conventional capacitors. They are perfect for energy storage and power backup in applications like electric cars and renewable energy systems because they have a low equivalent series resistance (ESR) and can supply high current.
- Variable Capacitors: Used in radio tuners and oscillators, among other devices where the frequency has to be adjusted, these capacitors have tunable capacitance values. They are available in two varieties: trimmer capacitors, which have three fine-tuning leads, and tuning capacitors, which feature a fixed rotor and spinning stator.

What Does a Capacitor Do on a Circuit Board
Capacitors on circuit boards fulfill various roles depending on their type and placement.
They are commonly used for decoupling and filtering purposes, reducing noise and interference in power supplies.
Capacitors also assist in signal coupling, allowing the transfer of AC signals while blocking DC components. Furthermore, they aid in voltage regulation, maintaining a steady voltage level for sensitive components.
In a word, capacitors contribute to the stability, functionality, and longevity of electronic devices.

Why Capacitor on Circuit Board Are So Important
Circuit board capacitors are essential components in electronic devices, enabling energy storage, voltage regulation, noise reduction, signal processing, power factor correction, and other vital functions. Their presence and proper selection contribute to the performance, reliability, and longevity of electronic systems.
Energy Storage: Capacitors store electrical energy and release it when needed. They act as temporary power reservoirs, providing energy to electronic components during high-demand situations and stabilizing voltage levels.
Voltage Regulation: Capacitors help regulate voltage levels in electronic circuits. They can absorb voltage spikes or surges, preventing damage to sensitive components, and release stored energy during voltage drops, ensuring a stable power supply.
Filtering and Noise Reduction: Capacitors act as filters, removing unwanted noise and interference from power supplies or signals. They can block high-frequency noise and prevent it from affecting the performance of other components, ensuring cleaner and more reliable signals.
Consequences of Capacitor Failure on a Circuit Board
When a capacitor fails on a circuit board, it can have serious consequences.
One typical problem is power supply instability, which can result in irregular device behavior or even outright failure.
Failed capacitors can generate voltage ripples, which influence the operation of other components and disturb the device's general functionality.
A defective capacitor may also generate excessive heat or leak electrolytes, causing damage to other components and jeopardizing the circuit board's stability.

How to Tell If a Capacitor is Bad on a Circuit Board?
Several indicators can help determine if a circuit board capacitor is faulty.
Physical signs such as bulging, leaking, or a pungent odor are clear indications of capacitor failure. Visual inspection of the capacitor's condition, such as checking for signs of corrosion or damage, can also provide insights.
Furthermore, specialized equipment like a capacitance meter or an oscilloscope can be used to measure capacitance values and assess the health of capacitors accurately.

Capacitor PCB Layout Considerations
Capacitor layout on a PCB is critical for circuit stability and performance.
- To reduce inductance, place decoupling capacitors adjacent to the IC power pins. For high-frequency applications, use numerous tiny caps.
- To protect against noise on multilayer boards, provide a ground or DC voltage layer between the power and signal layers.
- To avoid signal skew, maintain constant match lengths and trace impedances for differential pairs.
- When routing across plane splits, stay away from using ground planes for low impedance return links.
- In order to ensure symmetric placement for high-speed serial communications, AC coupling capacitors are necessary.
- Reduce crosstalk by using test points sparingly and using caution while routing signals.
- Keep the reference plane continuous and address thermal problems by orienting components correctly and using copper areas to dissipate heat.
- Always follow the advice from datasheets that is unique to your equipment.
Careful attention to placement, orientation, and routing helps capacitors function optimally and avoid short circuits or excessive parasites.
How to Solder PCB Capacitors on a Circuit Board
Soldering PCB capacitors is a straightforward process. Just need some easy steps.
1. Use a de-soldering braid to clean the pads and leads of the components. De-solder the component's leads from the board.
2. Use flux to clean and prepare the pads for soldering. Make sure there is enough flux on each pad to ensure that the component is securely held in place by capillary action.
3. Heat one pad at a time with your soldering iron, then apply the solder until it melts and flows into the pad. Repeat for all four pads, making sure they are adequately filled with solder paste.
Safe Handling of PCB Capacitors
It is crucial for anyone working with printed circuit boards (PCBs) to be aware of the safe handling procedures and potential hazards associated with PCB capacitors.
One of the primary hazards is the risk of electric shock, as PCB capacitors can store large amounts of voltage. It is essential to use protective equipment and thoroughly check all connections and wiring before use.
Another significant risk is the possibility of accidental fire, which can be mitigated by ensuring the capacitors are appropriately rated and properly connected.
Additionally, PCB capacitors may contain hazardous materials, so proper precautions and disposal methods must be followed.
Summing Up
Circuit board capacitors are crucial to assuring the best performance and dependability of electronic equipment. Their capacity to store and release electrical energy, adjust voltage, and filter out noise is extremely significant. Recognizing the significance of capacitors, understanding the repercussions of their failure, and knowing how to identify damaged capacitors are all critical components in ensuring the performance and durability of electronic systems.

Disclaimer: The views and opinions expressed by individual authors or forum participants on this website do not represent the views and opinions of Chipsmall, nor do they represent Chipsmall's official policy.

share this blog to:

