OUTLINE:
10 Must-Have Components Of A Distributor In A Vehicle
 4392
4392Still confused about the components of a distributor? Well, you’ve come to the right place.
This blog post delves into the components, types, and workings of a distributor, providing valuable insights for understanding and maintaining this crucial automotive component.
What Is A Distributor
A distributor is an electrical and mechanical device that is used in the ignition system of internal combustion engines.
Its main function is to route electricity from the ignition coil to each spark plug at the correct time
List of Components Of A Distributor In A Vehicle
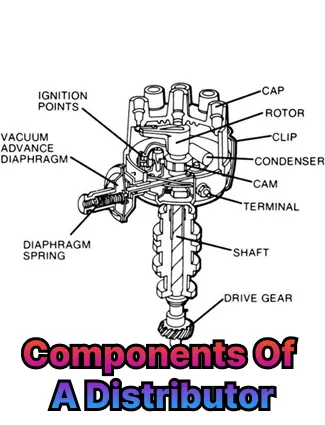
A vehicle's distributor consists of several key components, these components include:
1. Distributor Housing: The housing serves as the structural base for the distributor, encasing all the internal components and protecting them from external elements like dust and moisture. It's typically made of durable materials like aluminum or plastic.
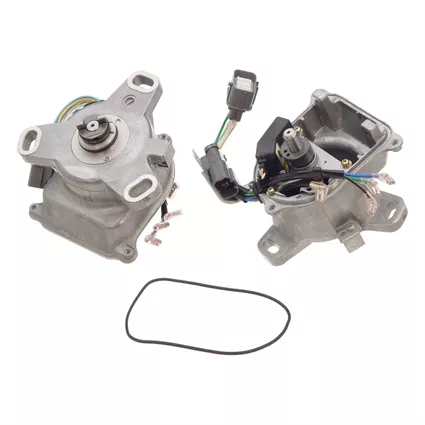

2. Distributor Shaft: This rotating shaft is directly connected to the engine's camshaft, enabling it to spin at half the camshaft's speed. The distributor shaft's rotation is crucial for the distributor's operation.
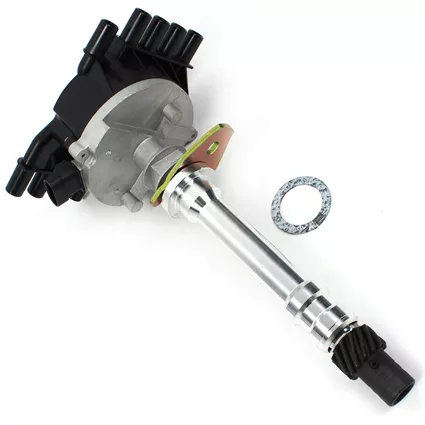

3. Rotor: The rotor is a small, rotating arm attached to the top of the distributor shaft. It has a contact tip that passes close to a series of stationary terminals inside the distributor cap.
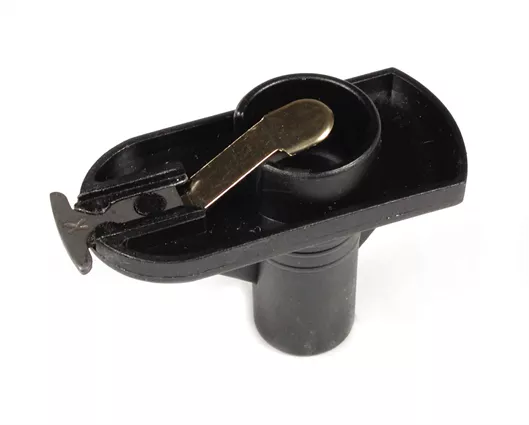

4. Contact Points: These are the electrical contacts that interrupt the flow of current to the ignition coil, creating the spark necessary for ignition. In older distributors, these are physical points that make and break contact, while in newer models, they are replaced by electronic sensors.
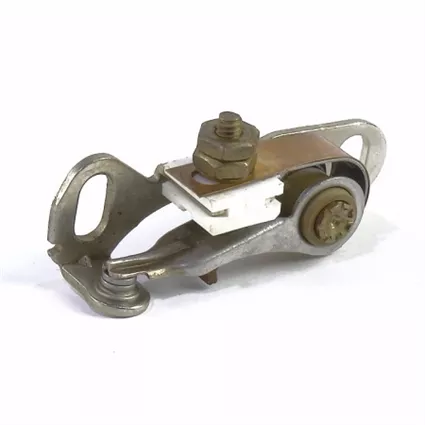

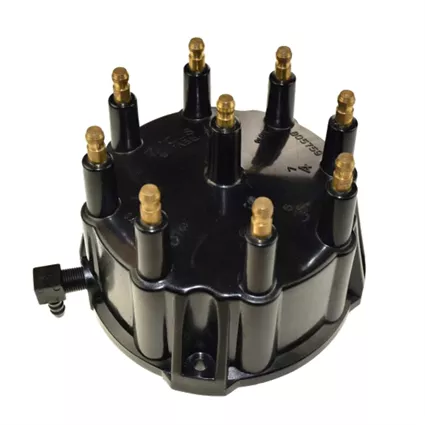
5. Distributor Cap: This is the insulating cover that sits atop the distributor housing. It houses the stationary terminals that the rotor tip contacts, ensuring proper distribution of high-voltage electricity.

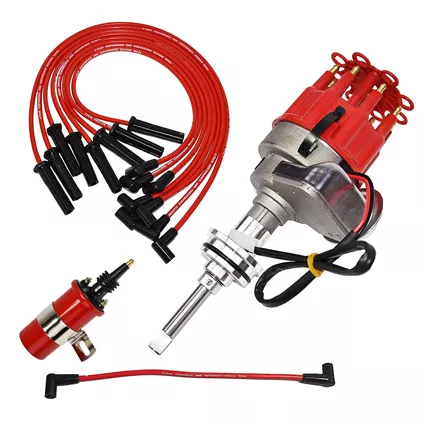
6. Spark Plug Wires: These are the insulated wires that carry the high-voltage spark from the distributor cap to the corresponding spark plugs in each cylinder.

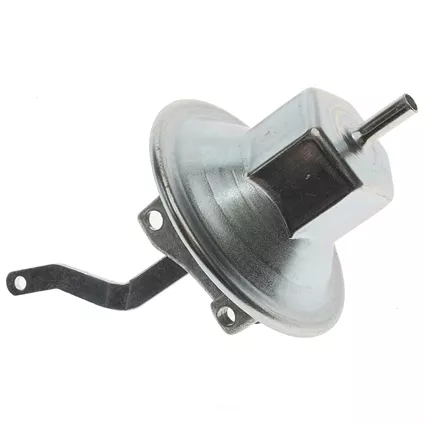
7. Vacuum Advance: This mechanism automatically adjusts the ignition timing based on the engine's vacuum level, improving engine performance and fuel economy.

8. Centrifugal Advance: This mechanism also adjusts the ignition timing based on engine RPM, preventing engine knocking at high speeds.
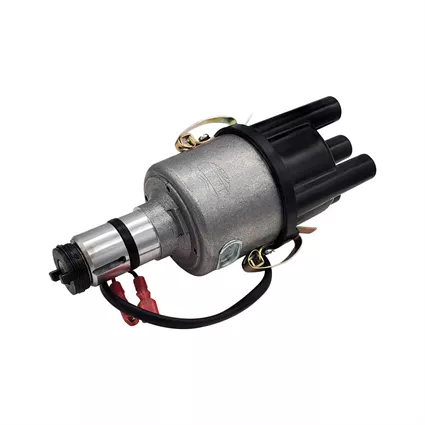

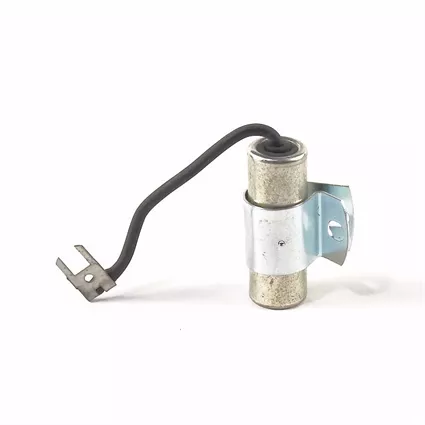
9. Condenser: In older distributors, a condenser is used to reduce electrical interference caused by the opening and closing of the contact points.

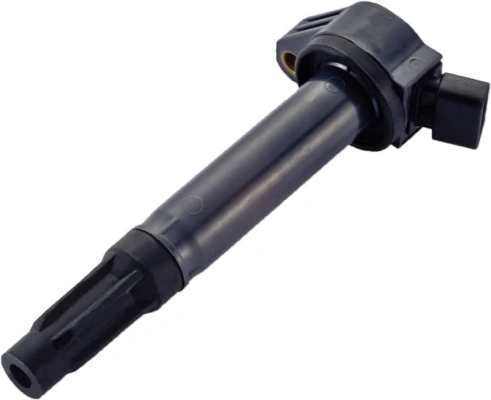
10. Ignition Coil: The ignition coil is a key component that generates the high-voltage spark required for ignition. It stores electrical energy and discharges it when the distributor's contact points open or the electronic sensors trigger.

How Many Types of Distributors
Due to the evolution of ignition technology, each type of distributor represents different stages.
Each type has its own advantages and disadvantages. Until now, there are three main types of distributors:
1. Mechanical distributors
Mechanical distributors use a set of contact points to interrupt the flow of current to the ignition coil. This creates a high-voltage spark that is sent to the spark plugs.
2. Electronic distributors
Electronic distributors use electronic sensors to control the timing of the spark. This makes them more accurate and reliable than mechanical distributors.
3. Distributorless ignition systems (DIS)
DIS systems do not use a distributor at all. Instead, individual ignition coils are used for each cylinder, which are controlled by the engine control module (ECM). This system is the most accurate and reliable, but it is also the most expensive.
How Does A Distributor Work
The distributor is driven by the engine's camshaft. As the camshaft rotates, it turns the distributor shaft, which in turn rotates the rotor. The rotor is a small arm that has a contact tip that rotates past a series of stationary contacts in the distributor cap.
When the rotor tip passes a contact, it completes the circuit to the ignition coil. This causes the coil to store electrical energy. When the rotor tip reaches the next contact, the circuit is broken, and the stored electrical energy is discharged in the form of a high-voltage spark.
The high-voltage spark is then sent to the spark plug for the corresponding cylinder. The spark plug ignites the air-fuel mixture in the cylinder, which causes the engine to produce power.
How to Maintain Distributor
Distributors require regular maintenance to ensure that they are working properly.
This typically involves inspecting the distributor cap and rotor for wear and tear, and replacing them if necessary. You should also check the distributor points and adjust them if necessary.
Signs of A Distributor Problem You Should Notice
There are a few signs that may indicate that your vehicle's distributor is not working properly:
- The engine is misfiring or running rough
- The engine is difficult to start
- The engine stalls or backfires
- The engine check light is on
If you experience any of these problems, it is important to have your vehicle's distributor checked by a qualified mechanic.
Wrapping Up
By understanding the components, types, and workings of a distributor, you can gain valuable insights into the heart of your vehicle's ignition system. Hope this blog helps you to have a better understanding of components of a distributor. If you have any needs for electronic components, just contact us.
Chipsmall Limited is made up of a professional team with an average of more than 20 years' experience in electronic component distribution. Based in Hong Kong, we have already developed strong and mutually beneficial business partnerships with customers in Europe, America, and South Asia, delivering obsolete and hard-to-find components to satisfy their special requirements.
If you want to have more distributors to choose from>>TOP 10 Largest Electronic Component Distributors

Disclaimer: The views and opinions expressed by individual authors or forum participants on this website do not represent the views and opinions of Chipsmall, nor do they represent Chipsmall's official policy.

share this blog to:







