OUTLINE:
A Guidance: How to Build DIY CNC Router
 446
446In today's era of rapid digital development, Internet connectivity has become an indispensable part of people's lives.
In order to meet the individual needs of different users for network performance, DIY (do-it-yourself) CNC routers are gradually emerging, which provides a new solution for network enthusiasts with its high customizability and strong performance advantages.
Next, let's explore the charm of DIY CNC routers.
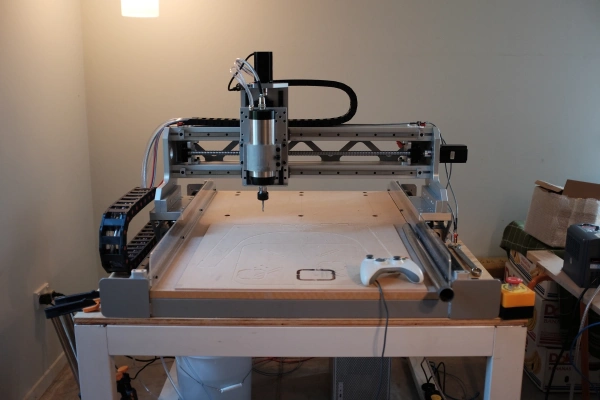
Image Source:Jeremy Young Design
How to Define A DIY CNC Router
The definition of a DIY CNC router is bellow:
A DIY CNC router can be defined as a router that is built and customized by users according to their personal needs and network environment by selecting, assembling and configuring corresponding hardware and software components.
This router not only meets user specific network requirements, such as higher network speed, stronger network coverage, more refined network management, but also provides a high degree of flexibility and customizability.
Users can deeply customize and optimize the router according to their own technical level and interests to achieve the best network performance and user experience.
DIY CNC routers emphasize user autonomy and creativity, allowing users to design and build the ideal network equipment according to their needs.
Applications&Working Principles
Here are some basic knowledge of CNC Router which may lay a foundation for building a diy CNC Router:
Applications:
It is mainly concentrated in industrial and commercial environments where stable, efficient and reliable network connectivity is required.
1.Industrial equipment monitoring and control:
CNC routers are widely used in industrial sites to achieve remote monitoring and control of large industrial equipment such as CNC machine tools and cranes.
Through the 4G/5G network, the operating data of these devices can be uploaded to the data management center in real time, so that managers can keep abreast of the operating status of the equipment and make necessary adjustments and optimizations.
Once the device fails or is abnormal, the CNC router is able to quickly send an alert to the data management center for timely response and processing.
2.Intelligent parking Monitoring:
In the intelligent parking lot, the CNC router can connect the collector and other equipment to automatically collect the information of vehicles and the number of empty parking Spaces.
This information can be uploaded to the control center in real time through the CNC router, and synchronized to the cloud platform, so that users can query, reserve the remaining parking space and pay parking fees at any time through the mobile APP.
3.Cash register equipment monitoring:
In restaurants, retail and other places, CNC routers can be used as a backup of the wired network to ensure that the cash register equipment can still work normally when the network is unstable.
The stable network connection provided by the CNC router can ensure the smooth and efficient user payment process, reducing the case of payment delays or failures.
4.Medical Equipment Monitoring:
In medical places such as hospitals, CNC routers can be connected to medical equipment to transmit equipment operation data and patient information in real time.
Medical staff can check the operation of the equipment at any time through the computer, and adjust and optimize it as needed.
Working Principles:
The working principle of CNC routers can be summarized as the following key steps, which together ensure the efficient and accurate transmission of data in the network:
1.Receive data packets:
When a CNC router receives a packet from another network device, such as a computer, server, or other router, it first checks the header information of the packet.
The header information contains important information such as the destination IP address, which is crucial for the subsequent processing of the router.
2.Route lookup:
A CNC router has one or more Routing tables that record information about the best path to each destination in the network.
The router looks in the routing table based on the destination IP address in the packet to determine which exit Interface the packet should be forwarded through.
During the search, the router finds the record that best matches the destination IP address and determines the forward path.
3.Forward the packet:
Once the forward path and exit interface are determined, the router's Forwarding Engine forwards the packet from the input interface to the correct exit interface.
This process usually involves the encapsulation and de-encapsulation of the packet to ensure the integrity and security of the packet during transmission.
4.Update the routing table:
CNC routers update their routing tables periodically or according to network changes.
This can be done through static route configuration, dynamic routing protocols (such as RIP, OSPF, etc.), or other means.
Routing table updates ensure that routers are able to select the best path for packet forwarding, thereby improving network performance and efficiency.
5.Network isolation and access control:
CNC routers can also achieve network isolation and access control functions.
By configuring access control lists (ACLs) and other security policies, routers can restrict or allow communication between specific devices or networks.
This helps protect network security against unauthorized access and data breaches.
6.Data processing and forwarding decisions:
In the whole process, the CNC router will parse and process the packet according to the network protocol (such as IP, TCP/UDP, etc.).
It will make forwarding decisions based on protocol regulations and routing table information to ensure that the packet can accurately reach the destination.
7.Performance and stability optimization:
CNC routers typically employ a range of techniques and algorithms to optimize performance and stability.
This includes queue management, congestion control, load balancing and other mechanisms to ensure efficient data transmission and forwarding under high load and complex network environments.
How to Build DIY CNC Router[Step by Step]
Building a DIY CNC router is a relatively complex process that requires a combination of hardware, software and network configuration knowledge. The following is a simplified DIY CNC router construction process:

Image Source: Instructables.com
1. Obtain hardware
- Router motherboard: Choose a router motherboard with stable performance and good scalability to ensure that it can meet the needs of CNC.
- Processor: Select a processor with a high CPU frequency and a large number of cores to ensure data processing capability and network throughput.
- Memory: Select a larger capacity of memory to increase the number of packets processed by the router at the same time.
- Flash: Select a large-capacity flash memory to provide enough space for system upgrades and configuration changes.
- Network interface: Select the type and number of wired and wireless interfaces according to your needs.
- Other hardware: such as cooling fans, protective rings, etc., to ensure the stable operation of the router.
2. Select software
- Operating system: Choose a stable and secure router operating system, such as OpenWrt, DD-WRT, etc.
- Router Management software: Choose a powerful, easy-to-use router management software for remote setup and monitoring.
3. Building process
(1) Hardware assembly: The router motherboard, processor, memory, flash memory and other hardware are assembled according to the instructions.
Install accessories such as cooling fans and protective rings to ensure the stable running of the router.
(2) System installation:
Install the operating system into your router's flash memory.
Install the router management software and perform the necessary configuration.
- Network configuration:
Configure the network interfaces of the router, including wired and wireless interfaces.
Set the Wi-Fi name and password to ensure network security.
- Function configuration:
Configure functions such as port forwarding and DNS Settings based on requirements.
Install and configure the necessary plug-ins and extensions to increase the functionality of the router.
- Firmware Update:
Check the firmware version of your router and make any necessary updates.
Ensure that your router's performance and security are up to date.
- Testing and optimization:
Test whether the network connection and functions of the router are normal.
Optimize and adjust according to the test results to improve the performance and stability of the router.
What Materials Does you Need to Build your CNC Router
Materials:
1.Router motherboard: This is the core part of the entire router, you need to choose a stable, reliable, good performance of the motherboard.
2.Processor (CPU) : Select a processor with a high frequency and a large number of cores to provide enough computing power to handle network traffic and routing tasks.
3.Memory (RAM) : The size of the memory will affect the number of packets processed by the router at the same time, so it is recommended to choose a memory with a larger capacity.
4.Flash Memory: Used to store the router's operating system and configuration files, you need to select a sufficient capacity of flash memory.
5.Network interface card (NIC) : Used to connect a wired network. You can select a multi-port NIC to meet the connection requirements of more devices.
6.Wireless module: If you need to support wireless network connectivity, you need to choose a compatible wireless module.
7.Antenna: For wireless modules, an antenna is needed to improve the coverage of wireless signals.
8.Power supply: Provide a stable power supply for the router to ensure that the router can operate normally.
Cooling devices, such as fans or heat sinks, are used to ensure that the router can maintain a low temperature during heavy load operation.
9.Shell: Used to protect the router's internal hardware, you can choose a metal or plastic shell.
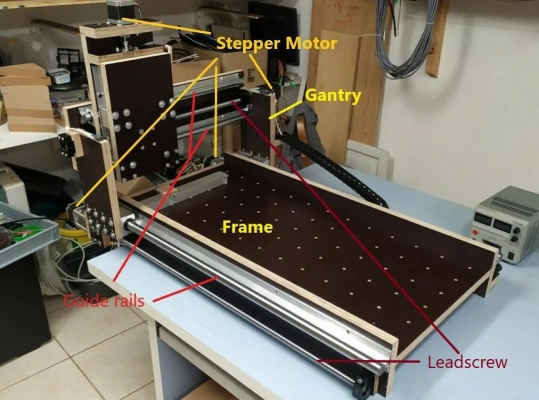
Image Source:AII3DP
Tools:
1.Screwdriver: Used to install and remove hardware.
2.Welding tools: If welding is required (for example, connecting antennas), prepare welding tools.
3.Network cable pliers: Used to make network cable ports.
4.Network cable: Used to connect routers and other network devices.
5.Computer: Used to configure routers, install operating systems and set network parameters.
Is It Worthy for Building A CNC Router by yourself
Whether a DIY CNC router is worth it mainly depends on individual needs and interests. If you have a strong interest in networking technology and devices, like to get your hands on and explore new technologies, then DIY CNC routers are definitely an option worth trying.
Through DIY, you can choose the most suitable hardware and software according to your needs and budget, and customize the router to meet your requirements, so as to obtain higher performance, stronger customizability and better learning experience.
However, DIY also requires a certain technical foundation and patience, if you are not familiar with this or limited time, then buying an off-the-shelf router may be more convenient and practical.
Therefore, whether it is worth DIY CNC router, you need to weigh the pros and cons according to your actual situation.
Final Verdict
Building a DIY CNC router is a challenging project that allows high performance, flexible routers to be customized to individual needs.
This will not only improve the technical level, but also provide insight into how network equipment works.
However, this also requires a certain amount of technical knowledge and experience, as well as careful consideration of hardware and software choices.

Disclaimer: The views and opinions expressed by individual authors or forum participants on this website do not represent the views and opinions of Chipsmall, nor do they represent Chipsmall's official policy.

share this blog to:

