OUTLINE:
Do you know these 5 basis types of passive component?
 1152
1152Have you ever wondered how electronic circuits work and what components are involved in their operation? Well, in the world of electronics, not all components are created equal. Some components have the ability to provide energy to a circuit, while others simply consume or dissipate energy provided by other components. These components are known as passive components, and they play a critical role in the functioning of electronic circuits. Examples of passive components include resistors, capacitors, inductors, transformers, and diodes.
Passive components refer to electronic components that do not have the ability to provide energy to an electronic circuit. Instead, they only consume or dissipate energy that is provided by other active components in the circuit. Examples of passive components include resistors, capacitors, inductors, transformers, and diodes.
Passive components have a wide range of applications across various electronic devices and systems. Here are some common examples of how passive components are used:
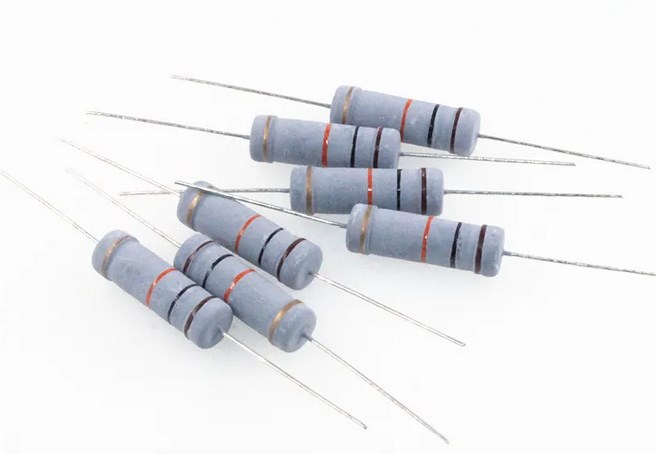
Resistors: the most basic type of passive component and are used to limit current flow, adjust signal levels, and reduce noise in electrical circuits.
Some common examples of resistors in daily life include:
LED lights: The resistors are used to limit the current flowing through the LED to prevent damage.
Electric heaters: Resistors are used to convert electrical energy into heat energy to warm up the surroundings.
Volume control on audio devices: Resistors are used to control the volume of the audio output.
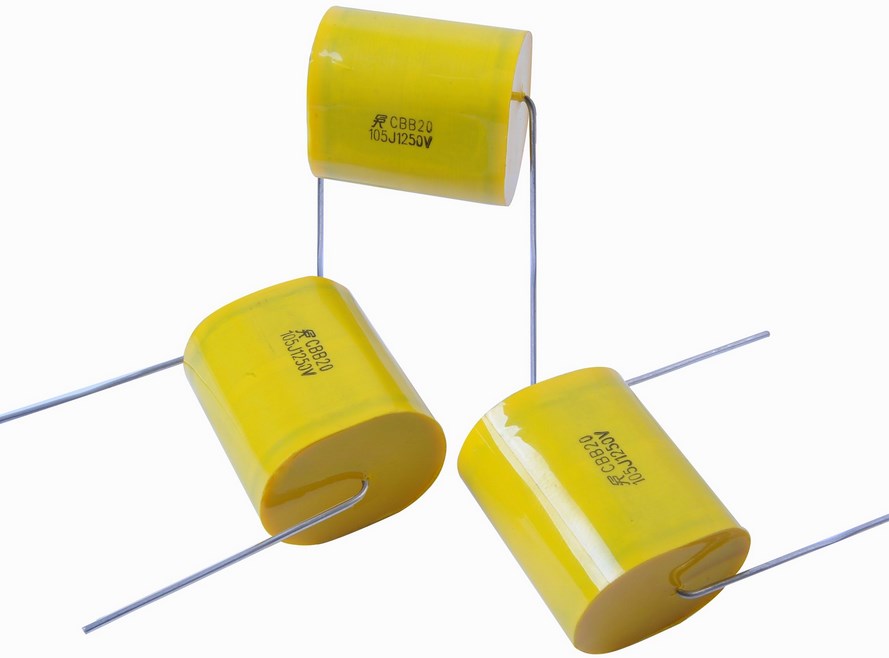
Capacitors: store and release electrical energy, filter out noise, and stabilize voltage levels in power supplies. They come in various capacitance values and voltage ratings.
Some common examples of capacitors in daily life include:
Camera flash: Capacitors are used to store electrical energy and release it quickly to produce a bright flash of light.
Power factor correction: Capacitors are used to improve the efficiency of power transmission by correcting the power factor in AC circuits.
Resonant circuits: Capacitors are used in resonant circuits to produce a specific frequency of oscillation.
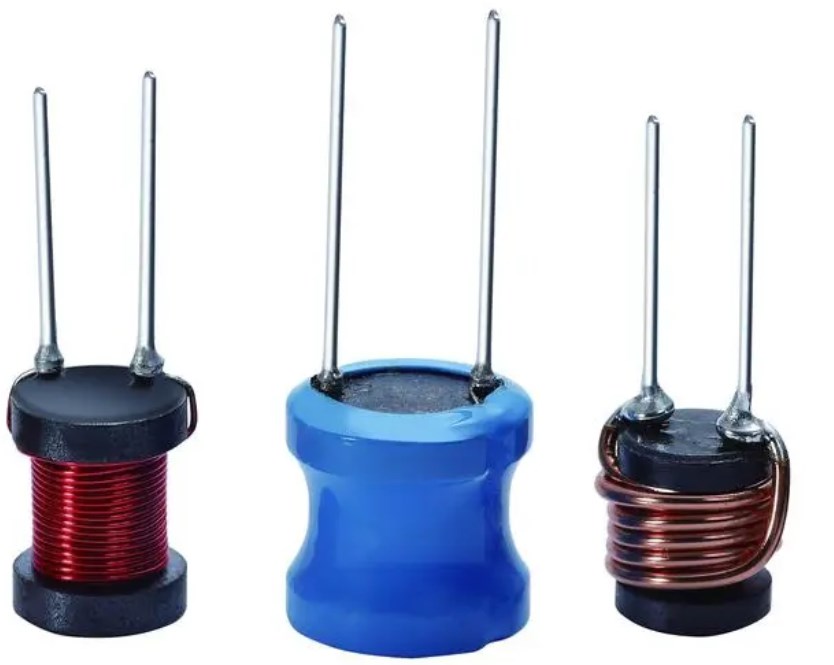
Inductors: store and release energy in the form of magnetic fields, filter out high-frequency signals, and regulate current flow.
Some common examples of inductors in daily life include:
Transformers: Inductors are used in transformers to step up or step down the voltage in AC circuits.
Speakers: Inductors are used in speakers to filter out unwanted frequencies and produce high-quality sound.
Electric motors: Inductors are used in electric motors to convert electrical energy into mechanical energy.

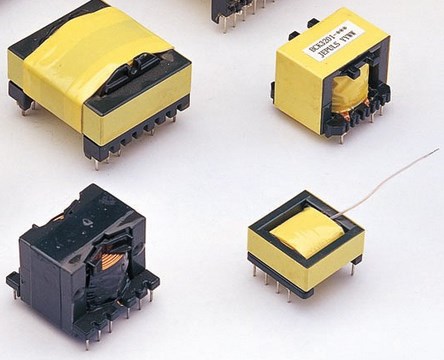
Transformers: transfer electrical energy from one circuit to another through electromagnetic induction, and are commonly used in power supplies and audio amplifiers.
Some common examples of transformers in daily life include:
Power adapters: Transformers are used in power adapters to convert high-voltage AC power to low-voltage DC power.
Doorbells: Transformers are used in doorbells to step down the voltage of the AC power supply to a safe level.
Neon signs: Transformers are used in neon signs to step up the voltage to a level sufficient to ionize the gas in the tubes.
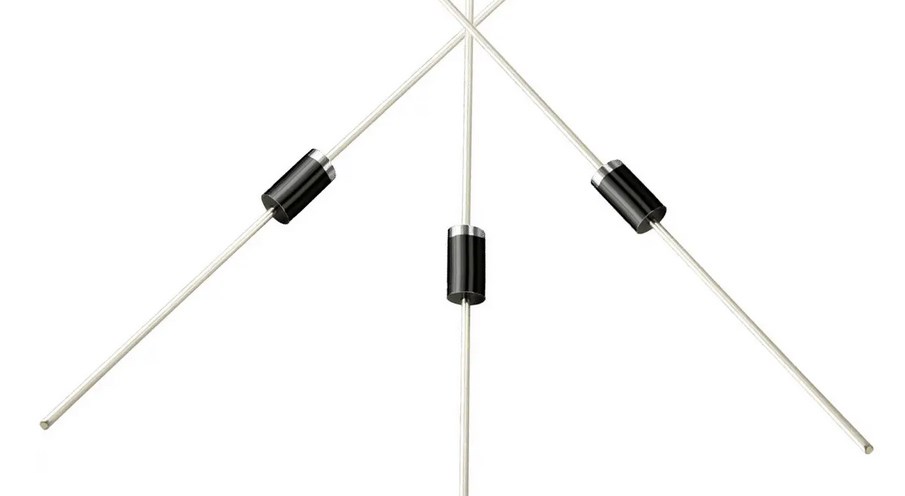
Diodes: allow current to flow in only one direction, and are commonly used in rectifiers and voltage regulators.
Some common examples of diodes in daily life include:
LEDs: Diodes are used in LEDs to emit light when an electric current flows through them.
Solar panels: Diodes are used in solar panels to prevent the flow of current in the opposite direction and protect the panels from damage.
Rectifiers: Diodes are used in rectifiers to convert AC power to DC power by allowing current to flow in only one direction.

Passive components are fundamental building blocks of electronic circuits and are ubiquitous in modern electronics. They enable engineers to design complex systems with precise control over signal levels and timing, and are essential for ensuring reliable and efficient operation of electronic devices.

Disclaimer: The views and opinions expressed by individual authors or forum participants on this website do not represent the views and opinions of Chipsmall, nor do they represent Chipsmall's official policy.

share this blog to:

