OUTLINE:
How Does a Light Sensor Work: Function, Types and Application
 398
398If there is a world shrouded in perpetual darkness, where streetlights never flicker on and our smartphones remain stubbornly dim. Light sensors play a crucial role in banishing this perpetual gloom, but have you ever stopped to wonder how does a light sensor work? In this article, we will explore the science behind how does light sensor work, their applications, and where they are commonly found.
What is a Light Sensor
Light sensors, also known as photodetectors or photoresistors, are electronic devices that detect and measure light levels in their surroundings.
The intensity of light affects the number of electrons emitted, resulting in a corresponding change in the electrical signal produced by the light sensor. Light sensors are used in a wide range of applications of modern technology, from simple light-sensitive switches to advanced imaging systems. These sensors convert light (visible or invisible) into an electrical signal, which can then be measured, processed, or used to control other devices.
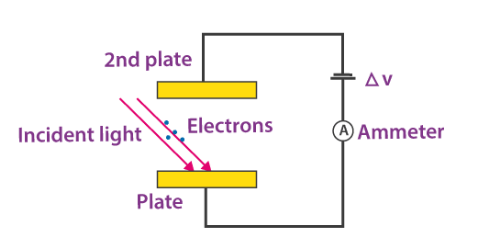
It utilizes the photoelectric effect, which is the emission of electrons when certain materials are exposed to light. They play a crucial role in various applications, from adjusting screen brightness on smartphones to controlling streetlights based on ambient light conditions. Their ability to perceive changes in light intensity makes them invaluable in creating responsive and adaptive systems.
Types of Light Sensors
Light sensors come in various types, each with unique characteristics and applications. Understanding these types can help in selecting the right sensor for specific needs.
Photodiodes
Working Principle: Generate current when exposed to light.
Applications: Light meters, optical communication devices, and industrial automation.
Phototransistors
Working Principle: Amplify current generated by light exposure.
Applications: Light detection in cameras, safety systems, and light-sensitive switches.
Photoresistors (LDRs)
Working Principle: Change resistance based on light intensity.
Applications: Street lighting, nightlights, and outdoor clocks.
Photovoltaic Cells
Working Principle: Convert light directly into voltage.
Applications: Solar panels, calculators, and renewable energy systems.
Other Types
Optical Sensors: Used in fiber optic communication.
Infrared Sensors: Detect infrared light for remote controls and motion detectors.
How Does a Light Sensor Work
Light sensors work in a variety of ways. The basic principle behind light sensors is the photoelectric effect, where light energy is converted into electrical energy. Depending on the type of light sensor, the working mechanism can vary:
Photodiodes
Photodiodes are semiconductor devices that generate a current when exposed to light. They operate in reverse bias mode, meaning that they allow current to flow only when they are illuminated. When photons hit the semiconductor material, they excite electrons, creating electron-hole pairs that generate a current proportional to the light intensity. This electron flow produces a current, which can be measured and interpreted as a change in light intensity.
Phototransistors
Phototransistors work similarly to photodiodes but with added amplification. They have a light-sensitive base region that, when illuminated, allows current to flow between the collector and emitter. This amplified current is much stronger than that of a photodiode, making phototransistors ideal for applications requiring higher sensitivity.
Photoresistors (LDRs)
Photoresistors, or light-dependent resistors (LDRs), change their resistance based on the intensity of light falling on them. Made of semiconductor materials, their resistance decreases as light intensity increases. This change in resistance can be easily measured and used to control circuits.
Photovoltaic Cells
Photovoltaic cells, commonly known as solar cells, directly convert light into voltage. When light photons strike the cell, they excite electrons, creating an electric field across the layers of the cell. This electric field drives a current, generating electricity.
Where is the Sensor on a Light
The placement of light sensors depends on the specific application. In devices like smartphones or tablets, light sensors are often located near the front-facing camera or display to measure the ambient light levels and adjust the screen brightness accordingly. In automatic lighting systems, light sensors are typically positioned on outdoor fixtures or integrated into the circuitry of indoor light switches to detect changes in ambient light and trigger the appropriate response.
Light Sensor Applications
Light sensors are integral to many modern technologies, providing functionality and enhancing the efficiency of various systems. They are found applications in various fields, including:
Automatic Lighting Systems: Automatic screen brightness adjustment based on ambient light. Light sensors enable automatic control of lighting systems, adjusting brightness levels based on natural light conditions.

Photography: Light sensors in cameras help determine the optimal exposure settings by measuring the available light.

Environmental Monitoring: Light sensors are used in weather stations and environmental monitoring equipment to measure light levels for research and analysis.
Display Technologies: Light sensors in smartphones and tablets assist in adaptive brightness control, ensuring optimal viewing experiences.

Energy Conservation: Light sensors contribute to energy-efficient practices by controlling outdoor lighting based on daylight availability. They also contribute to renewable energy such as Solar Panels, Solar Water Heaters, Solar-Powered Devices and so on. Light sensors can convert sunlight into electricity for sustainable energy solutions and can use light sensors to optimize heating efficiency. They also provide charge batteries and power devices using solar energy.

Sum Up
In summary, light sensors operate based on the photoelectric effect, converting light into an electrical signal. These sensors play a vital role in various applications, from adjusting screen brightness to controlling lighting systems. Understanding how does a light sensor work helps us appreciate the technology behind light detection and its impact on our daily lives.

Disclaimer: The views and opinions expressed by individual authors or forum participants on this website do not represent the views and opinions of Chipsmall, nor do they represent Chipsmall's official policy.

share this blog to: