OUTLINE:
How Modules Work in Electronics
 210
210Modules play a crucial role in modern electronics, providing convenient and efficient solutions for integrating complex functionalities into electronic systems. From communication modules to sensor modules, their versatility and ease of use have made them indispensable components in various applications. In this article, we will explore the inner workings of modules, shedding light on how they function and contribute to the seamless operation of electronic devices.
Definition and Purpose of Modules:
Modules can be described as self-contained units that encapsulate specific functionalities or subsystems within a larger electronic system. They are designed to simplify integration, reduce development time, and enhance scalability. By encapsulating complex circuits, interfaces, or sensors, modules provide a plug-and-play solution that facilitates faster prototyping and accelerates time-to-market.
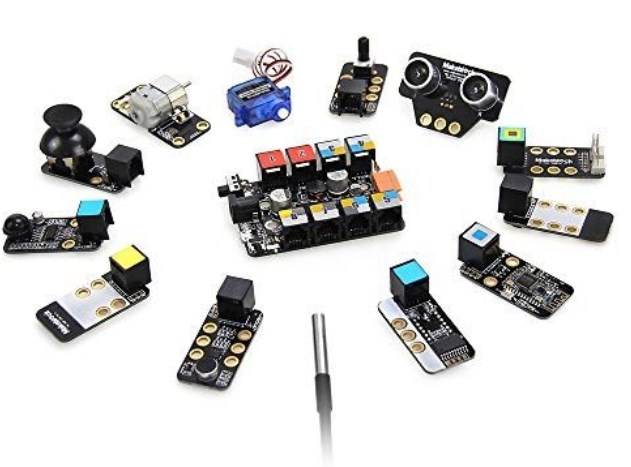

Functional Integration:
Modules achieve functional integration by combining various components, such as microcontrollers, sensors, communication interfaces, power management circuits, and more, into a single package. Through careful design and optimization, modules ensure seamless interaction between these components, enabling them to work together harmoniously.
Standardization and Interfacing:
Modules often follow industry-standard interfaces, ensuring compatibility and ease of integration with other electronic systems. Standardized communication protocols, pin-outs, and connectors simplify the process of connecting modules to host systems, reducing the need for custom wiring or complex interface designs.
Simplified Software Development:
Modules often come with preloaded firmware or software libraries that abstract the complexity of low-level programming tasks. This simplifies software development, allowing developers to focus on higher-level application logic rather than dealing with intricate hardware interactions. Modules with well-documented APIs and software development kits (SDKs) further simplify the integration process.
Flexibility and Scalability:
Modules offer flexibility and scalability, allowing designers to adapt and expand their systems without reinventing the wheel. As standalone units, modules can be easily swapped or upgraded, enabling system enhancements or the addition of new functionalities as project requirements evolve. This flexibility enhances the longevity and versatility of electronic systems.
Design Considerations:
Module design involves careful consideration of factors such as power consumption, form factor, heat dissipation, electromagnetic compatibility (EMC), and environmental ruggedness. These considerations ensure that modules are optimized for reliable operation in various conditions and can be seamlessly integrated into diverse applications.
Application Examples:
Modules find application in a wide range of industries and domains. They are used in wireless communication systems, Internet of Things (IoT) devices, robotics, industrial automation, medical devices, and more. For example, a Bluetooth module provides wireless connectivity, while a sensor module integrates multiple sensors for environmental monitoring or motion detection.

Advantages and Trade-offs:
While modules offer numerous advantages in terms of time-to-market, ease of integration, and scalability, they may have certain trade-offs. Modules may have higher cost compared to designing custom circuits, limited customization options, and may not always perfectly fit specific application requirements. Careful evaluation and selection of modules based on project needs are essential.
Conclusion:
Modules have revolutionized the electronics industry by simplifying integration, enhancing scalability, and accelerating development cycles. Through functional integration, standardized interfaces, simplified software development, and flexibility, modules empower designers to create innovative and efficient electronic systems. By understanding the inner workings of modules, engineers can harness their power to create robust and cutting-edge solutions in various domains.

Disclaimer: The views and opinions expressed by individual authors or forum participants on this website do not represent the views and opinions of Chipsmall, nor do they represent Chipsmall's official policy.

share this blog to:

