OUTLINE:
Level Sensors: Functional Characteristics and Main Types
 212
212In industries and various applications, the monitoring and control of fluid levels are critical for efficient operations and safety. Level sensors play a vital role in this regard, providing real-time data about the levels of liquids or solids in tanks, containers, or other vessels. This article explores what level sensors are, their applications, different types available, and factors to consider when choosing the right level sensor for specific needs.
Image Source: RealPars
What is a Level Sensor
A level sensor is a device designed to detect and measure the level of liquids, powders, or granular materials within a container or tank. These sensors are used to determine the volume, quantity, or presence of a substance at a particular level. Level sensors can be employed across various industries including manufacturing, chemical processing, food and beverage, pharmaceuticals, water treatment, and more.
What is a Level Sensor Used For
Level sensors serve several purposes in industrial and commercial settings:
Inventory Management: They enable accurate monitoring of material levels in storage tanks, helping to optimize inventory and prevent stockouts or overfills.
Process Control: Level sensors ensure consistent levels of liquids or solids in industrial processes, maintaining operational efficiency and quality.
Safety: They play a critical role in preventing overflow or dry running of pumps and equipment, thus enhancing safety and reducing downtime.
Environmental Monitoring: Level sensors are used in environmental applications such as monitoring water levels in reservoirs or detecting oil spills.
Types of Level Sensors
Level sensors come in various types, each suited for specific applications:
Capacitive Level Sensors: Capacitive level sensors measure the level of liquid by measuring the change in capacitance. This type of sensor has the advantages of stable structure, compactness, accuracy, and cheaper than other types of sensors, but it needs to be calibrated before use and can only detect certain liquids. Capacitive level sensors are often used in liquid storage tanks.
Ultrasonic Level Sensors: These sensors use ultrasonic waves to measure the distance to the surface of the material. They are suitable for non-contact level measurement of liquids and solids.
It emits a high-frequency ultrasonic pulse from the transducer (probe). When it encounters the surface of the measured medium, the ultrasonic wave is reflected, and the reflected wave is received by the same transducer and converted into an electrical signal. The ultrasonic pulse propagates at the speed of sound. The time interval from the emission to the reception of the ultrasonic pulse is proportional to the distance from the transducer to the surface of the measured medium.
Ultrasonic level meters are characterized by high reliability, high cost performance, and easy installation and maintenance. They are widely used in industries such as petroleum, mining, power plants, chemical plants, water treatment plants, hydrological monitoring, and environmental monitoring.
At the same time, ultrasonic level meters are not suitable for vacuum, changes in the propagation medium (such as strong volatility, etc.), high temperature, and high pressure.
Float Level Sensors: Float switches or sensors utilize a buoyant float that rises or falls with the liquid level. They are simple and cost-effective solutions for point level detection.
Radar Level Sensors: Radar sensors emit microwave signals and measure the time taken for the signal to be reflected back. They are highly accurate and can work in challenging environments.
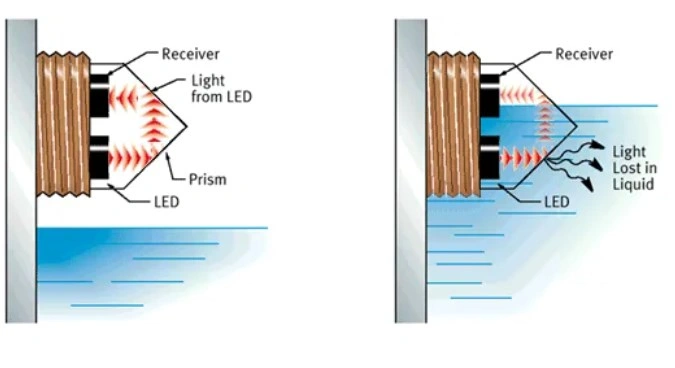
Optical Level Sensors: The optical liquid level sensor uses the principle of optical total reflection and refraction to measure the liquid level. When it is in a waterless state, the light is directly reflected from the internal transmitting tube back to the receiving tube; when it is in a watery state, the light emitted by the transmitting tube will be refracted into the liquid, and the receiving tube can only receive a small amount or no light at this time. It has the advantages of stable performance, high reliability, unaffected by high temperature and high pressure, and small size. Due to contact with liquid, the lens may become dirty, so it takes time to clean.
How to Choose a Level Sensor
Selecting the right level sensor depends on several factors:
Type of Material: Consider whether the sensor needs to measure liquids, solids, or both.
Range and Accuracy: Determine the required measurement range and the desired level of accuracy for your application.
Environmental Conditions: Assess the operating environment including temperature, pressure, and presence of corrosive chemicals.
Installation: Choose a sensor that can be easily integrated into your existing system or tank configuration.
Output Requirements: Consider the output signal (analog, digital) compatible with your control system.
Maintenance and Calibration: Evaluate ease of maintenance and calibration requirements.
Conclusion
In conclusion, level sensors are indispensable devices used across a wide range of industries to monitor and control fluid levels. Choosing the right level sensor involves understanding the specific application requirements, environmental conditions, and desired performance characteristics. By selecting the appropriate type of level sensor, businesses can enhance operational efficiency, improve safety, and ensure optimal utilization of resources.
Level sensors continue to evolve with advancements in technology, offering more accurate and reliable solutions for fluid and material level monitoring. As industries embrace automation and smart technologies, level sensors will play a crucial role in driving efficiency and sustainability in manufacturing and processing operations.

Disclaimer: The views and opinions expressed by individual authors or forum participants on this website do not represent the views and opinions of Chipsmall, nor do they represent Chipsmall's official policy.

share this blog to:





