OUTLINE:
Managing Heat Dissipation in PCBs
 161
161Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs) are the backbone of modern electronics, powering everything from smartphones to spacecraft. As electronic devices become smaller and more powerful, managing heat dissipation has become a critical challenge. Excessive heat can lead to component failure, reduced performance, and even safety hazards. In this article, we will explore techniques to effectively manage heat dissipation and prevent thermal issues in PCBs, including proper component placement, thermal vias, heatsinks, and thermal analysis tools.
Proper Component Placement
One of the fundamental techniques to control heat in PCBs is proper component placement. Careful positioning of heat-generating components can help minimize hotspots and improve overall thermal performance. Here are some guidelines:
a. Group heat-producing components: Cluster components that generate heat in close proximity. This reduces the spread of heat and enables more efficient cooling.
b. Keep high-power components near the board's edge: Placing power-hungry components near the edge of the PCB allows for easier integration with heatsinks or cooling fans.
c. Avoid blocking airflow: Ensure that components are not obstructing the airflow within the enclosure. Proper ventilation can significantly impact heat dissipation.
Thermal Vias
Thermal vias are copper-plated holes strategically located within the PCB. They play a crucial role in dissipating heat from components to other layers of the board or external heat sinks. Here's how they work:
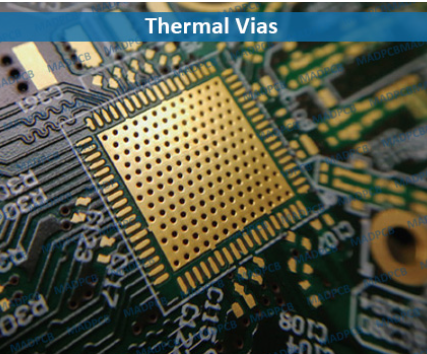
a. Heat transfer: Thermal vias conduct heat away from hotspots on the PCB to other layers with larger copper planes, where heat can be dissipated more effectively.
b. Enhanced cooling: Placing thermal vias under high-power components, like voltage regulators or processors, can substantially reduce their operating temperatures.
c. Optimization: Simulation and analysis tools can help determine the ideal placement and size of thermal vias for a specific PCB design.
Heatsinks
Heatsinks are passive cooling devices that absorb and dissipate heat away from hot components. They come in various shapes and sizes, and their effectiveness depends on proper installation. Key points to consider include:
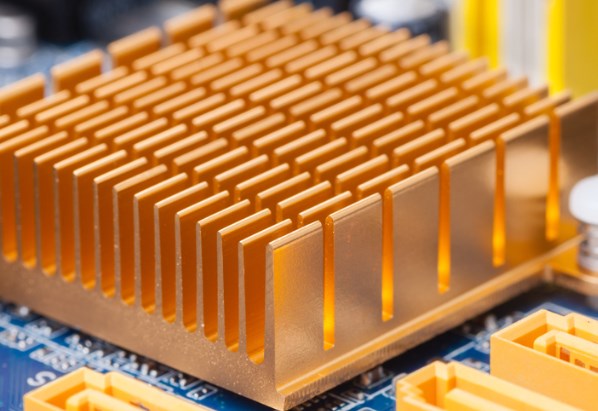
a. Match heatsinks to components: Choose heatsinks that match the thermal requirements of specific components. Larger heatsinks with greater surface areas are more efficient at dissipating heat.
b. Proper attachment: Ensure that heatsinks are securely and directly attached to the component's surface using thermal adhesive or thermal grease to maximize heat transfer.
c. Thermal resistance: Calculate the thermal resistance of the heatsink and its interface materials to optimize cooling performance.
Thermal Analysis Tools
Modern PCB design is greatly aided by thermal analysis tools that simulate and predict how heat will behave within a circuit board. These tools can identify potential hotspots and assist in optimizing heat dissipation. Some essential features of these tools include:
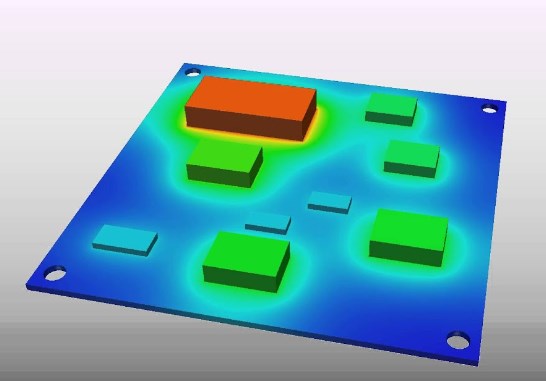
a. Simulation and modeling: Thermal analysis software allows designers to create virtual prototypes and test different heat management strategies before fabrication.
b. Iterative design: Engineers can make informed design decisions by analyzing the thermal performance of various component placements, materials, and cooling solutions.
c. Real-time monitoring: Some tools offer real-time monitoring of temperature and thermal performance during PCB operation, helping diagnose and address heat-related issues promptly.
Efficient heat dissipation is crucial for ensuring the reliability and performance of PCBs in today's electronics. By following best practices like proper component placement, thermal vias, heatsinks, and utilizing thermal analysis tools, engineers can mitigate thermal issues and extend the lifespan of electronic devices. As technology continues to advance, the importance of effective heat management in PCB design will only grow, making these techniques essential for the future of electronics.

Disclaimer: The views and opinions expressed by individual authors or forum participants on this website do not represent the views and opinions of Chipsmall, nor do they represent Chipsmall's official policy.

share this blog to:

