OUTLINE:
Matching Step-Up or Step-Down Transformers to Different Situations
 458
458Imagine a power plant generating electricity that needs to be efficiently delivered to homes and businesses far away. How does electricity travel such long distances without significant losses? This is where step-up and step-down transformers come into play. 
Transformers are essential devices in electrical power systems that enable efficient transmission and distribution of electricity. Among the various types of transformers, step-up and step-down transformers hold particular significance. In this article, we will delve into the differences between these two transformer types, exploring their functions, applications, design, and voltage conversion capabilities in more detail.
Step-Up Transformers:
Step-up transformers are designed to increase the voltage level of electricity. They take in power at a lower voltage and deliver it at a higher voltage. These transformers are commonly used in power generation plants, where they raise the output voltage of generators to a level suitable for long-distance transmission. By increasing the voltage, step-up transformers minimize power losses during transmission, as higher voltages result in lower current levels. This reduction in current helps to reduce resistive losses in power lines, making transmission more efficient. Step-up transformers are often found in substations and play a vital role in delivering electricity from the power plant to the grid.
Step-Down Transformers:
In contrast to step-up transformers, step-down transformers are intended to decrease the voltage level. They receive electricity at a higher voltage and deliver it at a lower voltage. Step-down transformers are prominent in distribution systems, where they lower the voltage to safe and usable levels for commercial, residential, and industrial consumers. They are commonly found on utility poles or in local substations, facilitating efficient power distribution and meeting the diverse voltage requirements of end-users. Step-down transformers also play a crucial role in isolating the electrical systems of different buildings or zones from each other, ensuring safety and preventing voltage fluctuations.

Voltage Conversion:
The fundamental distinction between step-up and step-down transformers lies in their voltage conversion capabilities. Step-up transformers increase voltage, whereas step-down transformers decrease voltage. This variation in voltage levels is crucial for effective power transmission and distribution, allowing electricity to be safely transported over long distances and utilized by end-users. Step-up transformers are typically used to raise the voltage from generators to high transmission levels, while step-down transformers are employed to reduce high transmission voltages to lower distribution voltages.
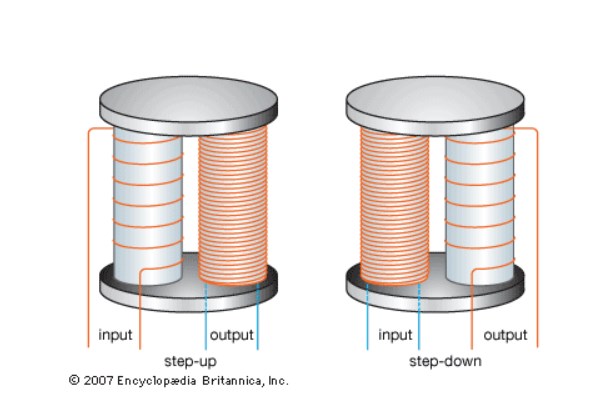
Transformer Design:
Step-up and step-down transformers possess distinct designs to cater to their respective functions. Step-up transformers are built with more primary windings than secondary windings, enabling them to step up the voltage. This design allows for a higher turns ratio, resulting in a voltage increase. On the other hand, step-down transformers have more secondary windings than primary windings, allowing them to step down the voltage. The design disparities reflect the transformer's ability to adjust voltage levels according to specific requirements.
Applications:
Step-up transformers are primarily employed in power plants, serving as generator step-up (GSU) transformers. They are instrumental in raising generator voltages for efficient transmission over long-distance power lines. Step-down transformers, on the other hand, are extensively used in distribution networks, ensuring that electricity reaches end-users at safe and usable voltage levels. They are employed in residential, commercial, and industrial settings to power appliances, machinery, and lighting systems. Step-down transformers can also be found in electronic devices, such as chargers, where they convert high-voltage AC power to lower-voltage DC power.
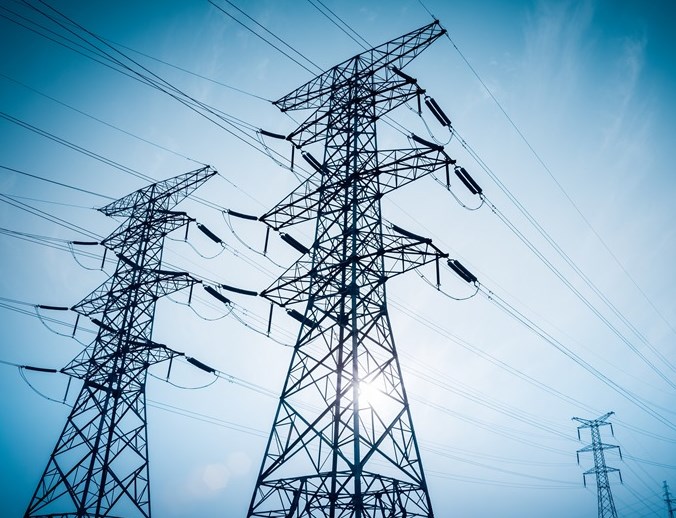


Step-up and step-down transformers are indispensable components of electrical power systems, each serving a unique purpose. Step-up transformers increase voltage levels for effective power transmission, while step-down transformers lower voltage levels for safe and efficient distribution. These remarkable devices help increase and decrease voltage levels, ensuring smooth transmission and safe distribution of electrical power in our daily life.

Disclaimer: The views and opinions expressed by individual authors or forum participants on this website do not represent the views and opinions of Chipsmall, nor do they represent Chipsmall's official policy.

share this blog to:

