OUTLINE:
Power Resistors: Understanding Their Importance and Applications
 327
327Resistors are an essential component in many circuit applications. However, not all resistors are suitable for every application, so careful selection is necessary.
To determine the resistance, tolerance, and voltage of a resistor, the resistor color code can be used. However, the power rating of the resistor is also a critical parameter that must be considered when selecting a resistor for use in a circuit. Using a resistor with an incorrect power rating can cause damage to the circuit, making it important to choose a resistor with the appropriate power rating.

What is the power rating of a resistor?
The power rating of a resistor is the maximum amount of energy that a resistor can safely dissipate without overheating or burning out. This is an important specification of a resistor and is sometimes referred to as the resistor wattage rating. According to Joule's first law, the electrical power generated is the product of the voltage across the resistor and the flow of current throughout the resistor.
How resistors are rated?
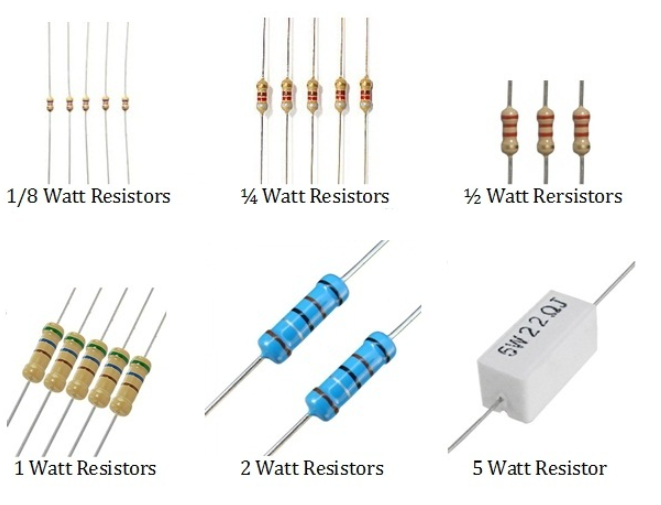
The power rating of a resistor is rated in watts, which is a unit of power. The power rating of a resistor is also referred to as its wattage. Generally, the larger the resistor, the more power it can handle. As the wattage of the resistor increases, so does its cost. Resistors can range in wattage from 1/8th watt to many kilowatts.
The power rating of a resistor is rated in watts, and it's also known as its wattage. The larger the resistor, the more power it can handle. Resistors can range in wattage from 1/8th watt to many kilowatts, and their cost increases with the wattage. The wattage of a resistor can be determined by its size, and resistors with high wattage are called power resistors.
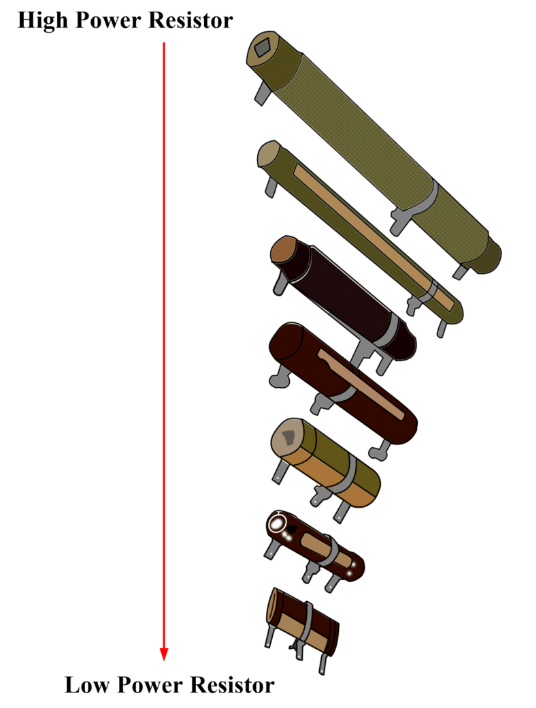
How to determine power rating of a resistor?
The power rating of a resistor can be determined by monitoring its package size. Through-hole resistors are typically available with 1/2W or 1/4W ratings, while power resistors are available with power ratings printed on them, such as 3W, 5W, and 25W.
For surface mount resistors, their power ratings can be determined by their size. Generally, 0603 and 0402 size resistors are rated with 1/16W, while 0805 size resistors can take 1/10W.
The power rating of a resistor can also be calculated using the electrical power formula, P = V * I, where 'V' is voltage and 'I' is current. From Ohm's Law, V = I * R, where 'R' is resistance. So, P = V * I can be expressed as P = I^2 * R or P = V^2 / R.
In summary, the power rating of a resistor can be determined by its package size or by calculating it using the electrical power formula and Ohm's Law.
Application of power resistors
Power resistors are resistors designed to dissipate higher power levels. They have higher power ratings and come in various specifications.
Power resistors are commonly used as:
Current limiting resistor in power supply circuits to limit the current through LEDs, transistors, etc.
Voltage divider resistors to generate intermediate voltages from a high DC supply voltage.
Load resistors in amplifier circuits to provide load to the output stage.
Bleeder resistors in capacitor circuits to discharge the stored charge in capacitors safely.
The main specifications that define a power resistor are:
Power rating: The maximum power the resistor can dissipate continuously.
Resistance value: Depends on the circuit requirements.
Tolerance: Margin of error in the resistance value.
Power resistors are available in different forms like axial leads, radial leads, surface mount, wire wound, etc. for use in different applications.
Advantages
High blocking accuracy.
Less noise during operation.
Stability& reliability.
low-temperature coefficient.
It can resist high temperatures.
It can work at an ambient temperature like 170 degrees Celsius.
Disadvantages
These resistors are large in size & weight.
These are expensive
Wire wound power resistors are not applicable beyond 200 kHz due to the interwinding capacitance & inductance.
Power resistors VS resistors
A power resistor is a type of resistor that is designed to handle higher power levels than standard resistors. Power resistors are typically used in applications where the resistor needs to dissipate a significant amount of power in the form of heat, such as in power supplies, amplifiers, and motor control circuits.
Power resistors are generally physically larger than standard resistors and are constructed using materials that can withstand higher temperatures. They may also have cooling fins or other features to help dissipate heat more effectively.
Standard resistors are available in a wide range of resistance values, tolerances, and power ratings, but they are not designed to handle the high power levels that power resistors can handle.
|
Power Resistors |
Resistors |
|
Generally larger |
Generally smaller |
|
High power levels |
Low power levels |
|
Requires effective heat dissipation |
Heat dissipation not a major concern |
|
These resistors are available in different types like a helical, grid, edge wound, chip or SMD, & water. |
Resistors are available in different types like, fixed, variable, wire wound, metal film, metal strip, metal oxide, etc. |
|
These are available in a compact physical package. |
Resistors are available in different types of package sizes & styles but the most frequently used one is SMD or rectangular surface mount. |
|
The power resistor dissipates a huge amount of power. |
The resistor doesn’t dissipate a huge amount of power. |
|
Used in power supplies, amplifiers, motor control circuits, and other high-power applications |
Used to set bias or gain, limit current flow, or divide voltages in low-power circuits |

Disclaimer: The views and opinions expressed by individual authors or forum participants on this website do not represent the views and opinions of Chipsmall, nor do they represent Chipsmall's official policy.

share this blog to:

