OUTLINE:
What Are Pull Up Pull Down Resistor
 465
465Digital circuits have three states: high level, low level, and high impedance. In some scenarios, it is desirable to initialize the voltage level to either high or low during power-up without encountering the high impedance state. This is achieved using pull up pull down resistor to stabilize the pins (while also providing current limiting). During the initial power-up of digital circuits, output states can be uncertain in terms of high and low logic levels. To ensure correct circuit operation, pull-up or pull-down resistors are used to stabilize these uncertain circuit states.
Pull-Up Resistor
A pull-up resistor connects to a power supply state. Simply put, it applies a high voltage to the point, raising its potential. Conversely, a pull-down resistor connects to the negative side, commonly to ground. When input port signals change due to different circuit forms, this change feeds back to the output port, resulting in an output status that should have been completed. However, when the input port has no signal, the output port remains in that state.
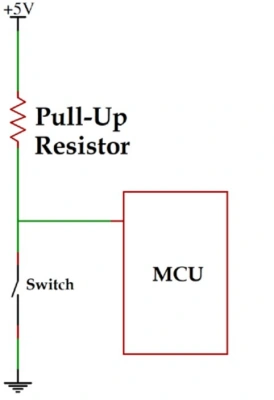
Image Source: robu.in
Functions
When TTL circuits drive CMOS circuits, if the high level output of the TTL circuit is below the minimum high level of the CMOS circuit (generally 3.5V), a pull-up resistor is needed at the TTL output to increase the high level output value.
Open-collector gate circuits must use pull-up resistors to increase the high level output value.
Some microcontroller pins also commonly use pull-up resistors to enhance output pin drive capability.
In CMOS chips, unused pins must not float to prevent damage due to static electricity. Pull-up resistors are typically used to lower input impedance and provide leakage paths.
Pull-up resistors on chip pins increase output levels, thereby improving the noise margin of chip input signals and enhancing interference resistance.
Enhances electromagnetic interference resistance of the bus; floating pins are susceptible to external electromagnetic interference.
Mismatched resistors in long-line transmission can cause reflections and interference. Pull-up and pull-down resistors provide impedance matching, effectively suppressing reflection interference.
Typical Pull-Up Resistor CircuitsThe diagram below illustrates a pull-up resistor circuit. This is a digital circuit inverter. When there is no low level input at the inverter input Ui, the pull-up resistor R1 stabilizes the input terminal at a high level, preventing possible low-level interference that could cause the inverter to operate incorrectly.
Pull-Down Resistor
Pull-down resistors connect an uncertain signal to ground, fixing it at a low level. When a device outputs current, it pulls down the current. When an IO port with a pull-down resistor is set to input mode, its default state is low level.
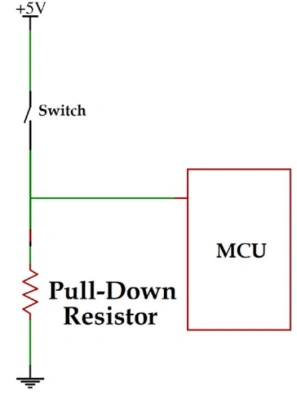
Image Source: robu.in
Functions
Raises voltage levels:
When TTL circuits drive CMOS circuits and the TTL circuit's high level output is below the CMOS circuit's minimum high level (generally 3.5V), a pull-up resistor is needed at the TTL output to raise the output high level value.
Open-collector gate circuits must use pull-up resistors to increase the high level output value.
Provides enhanced output pin drive capability. Some microcontroller pins also commonly use pull-up resistors.
Prevents static electricity and interference. In CMOS chips, unused pins should not float; usually, pull-up resistors are used to lower input impedance and provide leakage paths. Floating pins are susceptible to external electromagnetic interference.
Resistor matching and interference suppression: Mismatched resistors in long-line transmission can cause reflections and interference. Pull-up and pull-down resistors provide impedance matching.
Typical Pull-Down Resistor CircuitsThe diagram below shows a typical pull-down resistor circuit in a digital circuit inverter. The input terminal Ui is grounded through the pull-down resistor R1. This stabilizes the input terminal at a low level in the absence of a high-level input, preventing possible interference from high-level signals that could cause the inverter to operate incorrectly.
Recommended Resistance Values for Pull Up Pull Down Resistor
Power dissipation: The value of the resistor determines the current flowing through it when the button is pressed, which affects power consumption. If the resistance is too low, a high current will flow, leading to unnecessary power usage and heating of the device. To avoid this, it's important to choose a resistor value that limits the current appropriately, ensuring low power consumption.
Pin voltage when the switch is open: The pull-up resistor determines the voltage on the input pin when the switch is not pressed. If the resistance is too high and combined with a large leakage current from the input pin, the input voltage can become insufficient. This weak pull-up condition can cause issues. To prevent this, the pull-up resistor should be selected considering the input pin's impedance and leakage current.
For pull-up resistors, a commonly used guideline is to choose a resistor value that is at least 10 times smaller than the input pin impedance. In 5V logic devices, typical pull-up resistor values range from 1-5 kΩ. For switch and resistive sensor applications, values between 1-10 kΩ are often used.
As for pull-down resistors, their resistance should always be larger than the impedance of the logic circuit. Otherwise, the voltage will be pulled down excessively, resulting in a constant logical low value at the pin, regardless of the switch being on or off.
Conclusion
Mastering the basic knowledge of pull up pull down resistor can help with diagnosis and repair: disconnect the sensor from the wiring harness, measure the voltage of the ECU signal line, and determine or assist in determining whether the signal line is faulty, etc.

Disclaimer: The views and opinions expressed by individual authors or forum participants on this website do not represent the views and opinions of Chipsmall, nor do they represent Chipsmall's official policy.

share this blog to:





