OUTLINE:
Understand the Working Principle of Solenoid Valves Immediately
 194
194A solenoid valve is a crucial electromechanical device used for controlling the flow of fluids like liquids or gases. Its operation is based on the principle of electromagnetism, where an electric current is applied to a coil, generating a magnetic field that moves a plunger within a sealed chamber to open or close a valve mechanism. Understanding how a solenoid valve functions is essential for various applications across industries.
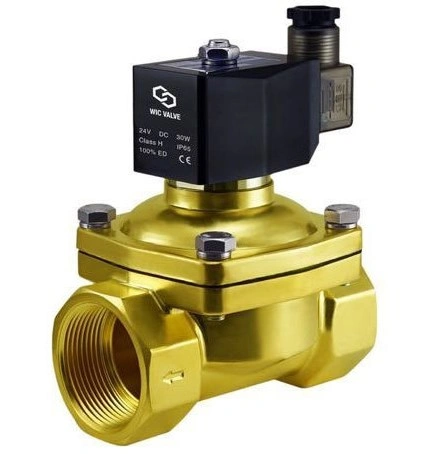

Image Source: SIO
What is a Solenoid Valve
A solenoid valve is an electromechanical device used to control the flow of fluids such as liquids or gases. It consists of a coil of wire (solenoid) wrapped around a movable ferromagnetic core (plunger) within a sealed chamber. When an electric current is applied to the coil, it creates a magnetic field that attracts the plunger, causing it to move and open or close a valve mechanism.
How Does the Solenoid Work
At its core, a solenoid works on the principle of electromagnetism. It consists of a coil of wire wrapped around a hollow core (often made of iron or steel). When an electric current flows through the coil, it generates a magnetic field within the core. This magnetic field, in turn, exerts a pulling or pushing force, depending on the design of the solenoid.
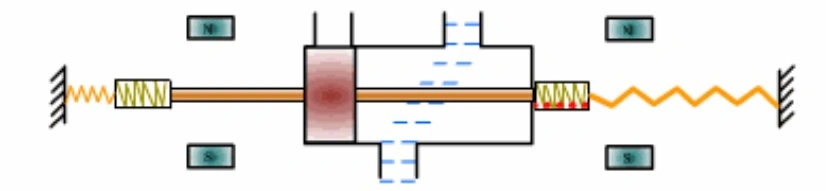
How Does a Solenoid Turn On Off
Inside the solenoid valve, there is a sealed chamber. This chamber has multiple through-holes at different positions, each connecting to different oil pipes. In the middle of the chamber, there is a piston, with two electromagnets on either side. When one side's electromagnet coil is energized, the valve body is attracted to that side. By controlling the movement of the valve body, different oil discharge passages can be opened or closed. The inlet oil passage is always open, allowing hydraulic oil to enter different discharge pipes. Then, the hydraulic oil pressure drives the piston of the hydraulic cylinder, which in turn drives the piston rod, ultimately driving the mechanical device. By controlling the current flow to the electromagnets, mechanical motion is controlled.
In short, When the current is turned on, the magnetic field attracts the plunger towards the coil, thereby opening or closing the valve mechanism connected to the plunger.
Conversely, when the current is turned off, the magnetic field dissipates, and the plunger returns to its original position either by a spring or by gravity, depending on the valve design.
Select a solenoid valve
Generally, a solenoid valve with a suitable pipe diameter should be selected according to the flow rate of the system, and its operating voltage, applicable ambient temperature, working pressure and other parameter requirements should also be considered. When installing the solenoid valve, the valve body of the solenoid valve should be perpendicular to the pipeline to ensure that the solenoid valve core can move up and down easily.
In order to ensure the tightness of the solenoid valve when it is closed, the flow direction of the medium in the system should be consistent with the nominal direction on the solenoid valve body. In addition, in order to prevent the solenoid valve core hole from being blocked by dirt, it is recommended to install a filter at the front end of the solenoid valve. The solenoid valve body should be fixed on the unit or bracket to avoid vibration and cause system leakage.
Differences Between Single Double Solenoid Valve
Single solenoid valve:
Has one solenoid coil.
Features spring resetting.
Switches on under constant power-on and air inlet.
Has two positions: one with no signal (spring position) and one with a signal (electromagnetic position).
Similar to a single-acting pneumatic cylinder.
Power-on side pulls, power-off side pushes.
Double solenoid valve:
Has two solenoid coils.
Requires the other coil to be energized for transposition.
Switches on at instant power-on.
Features a three-position valve: middle position with no signal, piston moves to the side with a signal.
Similar to a double-acting pneumatic cylinder.
No spring resetting.
Operates with one coil pulling and the other pushing.
For example, a single solenoid valve is suitable for applications like a cigarette lighter, while a double solenoid valve is used for oil guns. The control signals differ based on the requirements of the solenoid valve's operation.
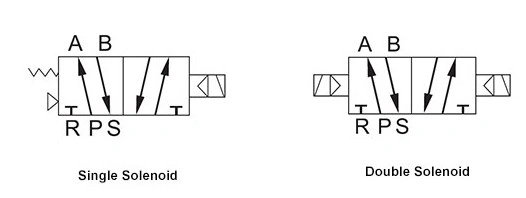
Image Source: Solenoid Valves
What Happens When a Solenoid Valve Goes Bad
When a solenoid valve fails, it may present a variety of symptoms depending on the severity of the problem. Some prevalent difficulties and their potential implications are:
Failure to Open or Close: One of the most obvious indicators of a defective solenoid valve is the inability to open or close properly. The valve may become trapped in one position, either fully open or entirely closed, causing disturbances in fluid flow or system performance.
Leaking: A worn-out or defective solenoid valve can develop leaks, allowing fluid to escape even while the valve is supposed to be closed. This can result in fluid loss, lower system performance, and potential damage to nearby components.
Reduced Flow or Pressure: If the solenoid valve gets partially clogged or obstructed due to debris buildup or internal damage, it may restrict fluid flow or lower pressure, resulting in decreased system performance or malfunction.
Erratic Operation: A faulty solenoid valve may display erratic behavior, such as intermittent opening and closing or sudden variations in fluid flow. This can create system instability, resulting in inconsistent performance or operational failures.
Electrical Issues: Problems with the solenoid valve's electrical components, such as the coil or wiring, can also cause problems. This may include failing to properly activate or de-energize the coil, causing the valve to respond incorrectly or not work at all.
Noisy Operation: Excessive noise during the operation of the solenoid valve, such as buzzing or humming sounds, can indicate mechanical issues or misalignment of internal components, which may eventually lead to valve failure if left unaddressed.
FAQs
What does 5/2 solenoid valve mean?
"Two-position" indicates that the solenoid valve has two positions: open and closed.
"Five-port" means that there are five ports or channels available.
The two-position and five-port solenoid valve is usually used together with the double-acting pneumatic cylinder. To choose the single solenoid valve or the double one relies on the processing requirements.
Conclusion
Whether it's managing the flow of water in irrigation systems or regulating the flow of gases in manufacturing processes, solenoid valves play a vital role in modern technology. Understanding their operation and potential issues ensures efficient system performance and helps troubleshoot problems when they arise.

Disclaimer: The views and opinions expressed by individual authors or forum participants on this website do not represent the views and opinions of Chipsmall, nor do they represent Chipsmall's official policy.







