OUTLINE:
Know More about Symbol for a Coil
 714
714The electrical symbol for a coil is a fundamental element of electrical circuit diagrams. Understanding its meaning and variations is essential for anyone working with electronics. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the significance of coil symbols, their design, variations, practical applications, and the best resources to learn more.
Introduction to Electrical Symbols
Electrical symbols are the shorthand of electronics. They represent physical components or processes. Let's start with the coil symbol.
Electrical symbols serve as a universal language for engineers and electricians to represent components and connections in circuit diagrams. They provide a concise and standardized way to communicate complex circuit designs.
The Importance of the Coil in Electrical Circuits
Coils are crucial in electrical circuits. In this section, we will explore why they are so important.
The coil, also known as an inductor, plays a crucial role in electrical circuits. Its importance stems from its ability to store and release electrical energy in the form of magnetic fields. Here are some key aspects highlighting the importance of coils in electrical circuits:
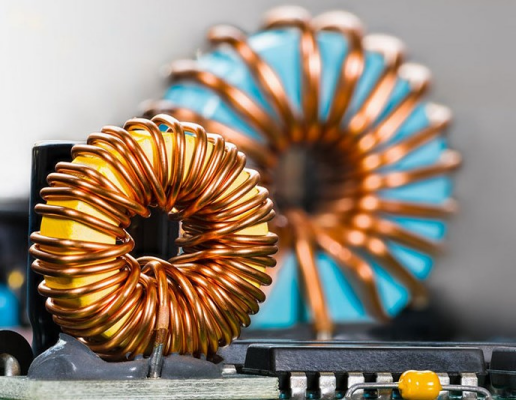
1.Energy Storage: Coils store energy in the form of a magnetic field when an electric current flows through them. This stored energy can be released back into the circuit when the current changes or is interrupted. This property allows coils to act as energy storage devices.
2. Inductance: Coils possess a property called inductance, which is a measure of their ability to store magnetic energy. Inductance is represented by the symbol "L" and is measured in henries (H). It determines how much current an inductor will induce in response to changes in the circuit.
3. Filtering and Signal Processing: Coils are commonly used in filters and signal processing circuits. They can pass or block specific frequencies of electrical signals based on their inductance and the characteristics of the circuit. Inductors are particularly effective in blocking high-frequency noise and allowing low-frequency signals to pass.
3. Voltage and Current Regulation: Coils are instrumental in regulating voltage and current in electrical circuits. By utilizing the property of inductance, coils can resist changes in current flow, thereby stabilizing the flow of electricity. They can smooth out fluctuations in current, reduce electrical noise, and protect sensitive components from damage.
4. Magnetic Fields: Coils generate magnetic fields when a current flows through them. These magnetic fields can be used for various purposes, such as creating electromagnetic devices like transformers, motors, and generators. Coils are essential components in these devices, enabling the conversion of electrical energy into mechanical energy and vice versa.
5. Timing and Oscillation: Coils are integral to the functioning of oscillators and timing circuits. They control the frequency and timing of oscillations by determining the rate at which energy is stored and released. This property is utilized in applications such as radio frequency circuits, timing circuits, and resonant circuits.
In summary, coils have significant importance in electrical circuits due to their ability to store and release energy, regulate voltage and current, filter signals, generate magnetic fields, and control timing. Their versatile properties make them essential components in a wide range of electronic devices and systems.
Detailed Look at the Symbol for a Coil
The coil symbol is simple but significant. In this section, we will examine it in detail.
1. Basic Design of the Coil Symbol
The electrical symbol for a coil typically consists of two parallel lines, often curved, representing the wire wound around a core. It indicates the presence of an inductor or a coil component in a circuit. Understanding its basic design is essential for interpreting circuit diagrams accurately.
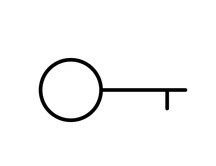
2. Variations in Coil Symbols
While the basic design of the coil symbol remains consistent, there may be variations in its representation. Different standards or cultural practices might influence the appearance of the coil symbol. Being aware of these variations ensures effective communication and collaboration among professionals worldwide.
3. Coil Symbols in Different Countries
Coil symbols can vary across countries due to regional conventions or standards. For example, some countries may use different line styles, orientations, or additional markings to represent coils. Familiarizing ourselves with these differences enables understanding and collaboration in a global context. Here are some commonly used coil symbols:
1. Inductor (Coil) Symbol:
(1) International Standard (IEC):
The coil symbol is represented by a rectangle with curved or straight edges. The two terminals are usually marked with "+" and "-" signs or labeled with the corresponding electrical designations.
(2) North America (ANSI/IEEE):
The coil symbol is represented by a series of zigzag lines within a rectangle. The terminals are typically marked with "+" and "-" signs or labeled with the corresponding electrical designations.
2. Transformer Symbol:
(1) International Standard (IEC):
The transformer symbol consists of two or more coils placed adjacent to each other. The primary and secondary windings are denoted by numbers and dots. The dots indicate the relative polarity of the windings.
(2) North America (ANSI/IEEE):
The transformer symbol is similar to the international standard, but the dots are replaced with small circles.
Practical Applications of Coils in Electronics
Coils are found in many electronic devices. After learning how they work, let's explore their applications.
1. Coils in Transformers
Transformers utilize coils to transfer electrical energy from one circuit to another through electromagnetic induction. Understanding the role of coils in transformers is vital for designing and analyzing power distribution systems efficiently.
2. Coils in Inductors
Inductors, consisting of one or more coils, store energy in a magnetic field. They find applications in various electronic devices, including filters, oscillators, and power supplies. Exploring the use of coils in inductors expands our understanding of their role in different electronic circuits.
3. Coils in Electromagnets
Coils form the foundation of electromagnets by generating a magnetic field when an electric current passes through them. Electromagnets are integral to numerous applications, from electric motors and relays to magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) machines. Understanding how coils enable electromagnetism broadens our knowledge of their practical implementations.
Final Verdict
In conclusion, understanding the symbol for a coil is essential for interpreting circuit diagrams accurately and effectively communicating circuit designs. We explored the significance of coil symbols, their basic design, variations, and practical applications. By grasping the intricacies of coil symbols can advance their knowledge and contribute to the development of electronic systems.

Disclaimer: The views and opinions expressed by individual authors or forum participants on this website do not represent the views and opinions of Chipsmall, nor do they represent Chipsmall's official policy.

share this blog to:

