OUTLINE:
The Components and Advantages of Microcontrollers
 349
349In today's fast-paced world, electronic devices have become an integral part of our daily lives. From smartphones to home appliances, we rely on these devices to make our lives more comfortable and convenient. One of the critical components of these electronic devices is microcontrollers. Despite their small size, microcontrollers play a vital role in controlling the specific functions of these devices, making them more efficient and cost-effective. In this article, we will explore the components and advantages of microcontrollers, shedding light on their importance in the modern world.
What is a Microcontroller?
A microcontroller is a small, integrated circuit that is designed to control a specific function in an embedded system. It contains a processor, memory, and input/output peripherals all on a single chip.
Microcontrollers, also known as embedded controllers or microcontroller units (MCUs), are used in a variety of devices such as vehicles, robots, medical equipment, home appliances, and vending machines. They are like mini personal computers that are programmed to control specific features of a larger component, without the need for a complex operating system.
Elements of Microcontrollers
A Microcontroller consists of the following components.
Central Processing Unit (CPU)
Program Memory (ROM – Read Only Memory)
Data Memory (RAM – Random Access Memory)
Timers and Counters
I/O Ports (I/O – Input/Output)
Serial Communication Interface
Clock Circuit (Oscillator Circuit)
Interrupt Mechanism
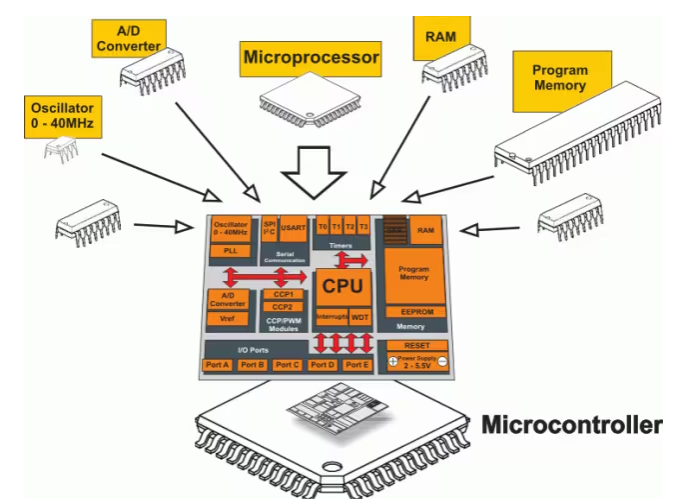
Basic Structure of a Microcontroller
The basic structure of a microcontroller consists of three major components: the CPU, memory, and I/O ports. The CPU is the brain of the microcontroller and consists of an Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU) and a Control Unit (CU). It reads, decodes, and executes instructions to perform arithmetic, logic, and data transfer operations.
Any computational system requires two types of memory: program memory and data memory. Program memory contains the program instructions to be executed by the CPU, while data memory is required to store temporary data while executing the instructions. Program memory is usually a Read Only Memory or ROM, while data memory is a Random Access Memory or RAM.
The interface for the microcontroller to the external world is provided by the I/O ports or Input/Output Ports. Input devices like switches and keypads provide information from the user to the CPU in the form of binary data. The CPU, upon receiving the data from the input devices, executes appropriate instructions and gives a response through output devices like LEDs, displays, and printers.
Another important component of a microcontroller is the system bus, which is a group of connecting wires that connect the CPU with other peripherals like memory, I/O ports, and other supporting components. Timers and counters are also important components of a microcontroller, providing time delays and counting external events. They can also provide function generation, pulse width modulation, clock control, and more.
A serial port is used to communicate with other devices and peripherals externally, and the most common serial communication implemented in microcontrollers is UART. Interrupts are also crucial, as they allow the microcontroller to respond to external or internal events.
Analog to Digital Converter (ADC) is a circuit that converts analog signals to digital signals. The ADC circuit forms the interface between the external analog input devices and the CPU of the microcontroller. Almost all sensors are analog devices, and their analog data must be converted into digital data for the CPU to understand. On the other hand, Digital to Analog Converter (DAC) works in contrast to ADC, converting digital signals to analog signals and forming the bridge between the CPU of the microcontroller and the external analog devices.
Advantages 
Low time required for performing operations
Easy to use, troubleshoot, and maintain
Can perform many tasks, saving human effort
Processor chip is small and flexible
Higher integration reduces cost and size of the system
Easy to interface additional RAM, ROM, and I/O ports
Can act as a microcomputer without any digital parts
Once programmed, cannot be reprogrammed
Disadvantages 
Generally used in micro equipment
More complex structure compared to microprocessors
Cannot directly interface with higher-power devices
Can only perform a limited number of executions simultaneously.
Conclusion
Microcontrollers are essential components of modern electronic devices, making them more efficient and cost-effective. They offer various advantages, including their ability to perform multiple tasks, small size, and ease of use. With the advancements in technology, the applications of microcontrollers are continually expanding, making them a crucial aspect of the modern world.

Disclaimer: The views and opinions expressed by individual authors or forum participants on this website do not represent the views and opinions of Chipsmall, nor do they represent Chipsmall's official policy.

share this blog to:

