OUTLINE:
The Importance of Testing and Discharging Capacitors: Ensuring Safe and Reliable Electronic Systems
 724
724Why We Need to Test Capacitor
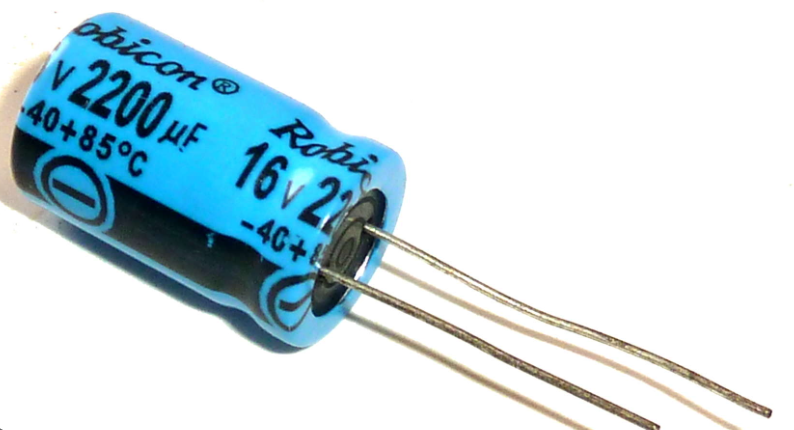
Capacitors can be classified into electrolytic and non-electrolytic types and are sensitive to voltage spikes. Electrolytic capacitors fail due to discharging too much current too quickly or drying out over time, while non-electrolytic capacitors fail due to leakages. Testing capacitors is important to ensure they are functioning properly and to prevent damage to other components in the circuit.
Why do Capacitors Need to be Discharged
Capacitors can store electric charge even when the main power supply is removed, making them dangerous to handle. Accidentally touching the leads of a charged capacitor can cause serious injury or even death. To prevent this, capacitors must be discharged before handling or disconnecting them. Short-circuiting a charged capacitor can also damage electronic components and other parts of the circuit.
Methods to Discharge Capacitor
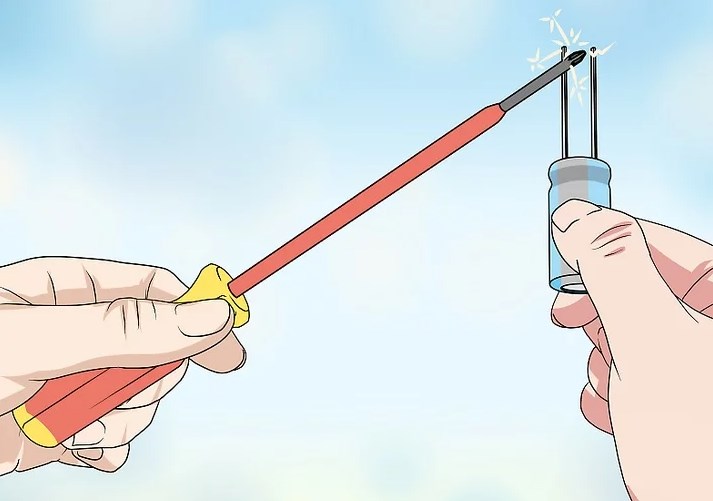
• Using a metal object like an insulated screwdriver by shorting the capacitor leads. This can discharge capacitors easily but is not the safest method.
• Using a bleeder resistor which is a safer, professional way to discharge a capacitor. The resistor value and power rating can be calculated using an online calculator based on the capacitor's capacitance, voltage rating and desired discharge time.
• Using a resistive load like a tungsten lamp rated for at least 10W to safely discharge the capacitor. The lamp will glow while the capacitor discharges and fade out once the capacitor is fully discharged.
Some Aspects to Consider When Discharging a Capacitor
Safety: Capacitors can store a significant amount of electrical energy, so it's important to discharge them safely to avoid electric shock. Always wear appropriate personal protective equipment and use caution when handling charged capacitors.
Discharge time: The time it takes to discharge a capacitor depends on the capacitance of the capacitor and the resistance of the discharge circuit. A larger capacitor will take longer to discharge than a smaller one, and a higher resistance discharge circuit will take longer to discharge the capacitor.
Discharge circuit: A discharge circuit is needed to safely discharge a capacitor. A common way to discharge a capacitor is to use a resistor connected across the capacitor terminals, which will allow the stored charge to slowly dissipate.
Voltage rating: Capacitors have a maximum voltage rating, which should not be exceeded during discharging. Exceeding the voltage rating can cause the capacitor to fail or even explode.
Discharge direction: Capacitors can be polarized or non-polarized, and the discharge direction will depend on the type of capacitor. For polarized capacitors, the negative terminal should be discharged first, while for non-polarized capacitors, either terminal can be discharged first.
Discharge current: The current during discharge can be quite high, especially for large capacitors. It's important to ensure that the discharge circuit can handle the current without overheating or failing.
Discharge monitoring: It's a good idea to monitor the voltage across the capacitor during discharge to ensure that it is fully discharged. A voltage meter or oscilloscope can be used for this purpose.
.jpg)

Disclaimer: The views and opinions expressed by individual authors or forum participants on this website do not represent the views and opinions of Chipsmall, nor do they represent Chipsmall's official policy.

share this blog to:

