OUTLINE:
All Types of Thermal Fuses Here
 669
669Thermal fuses are known as thermal cut-offs, these fuses prevent equipment from overheating by opening circuits to cut off power. They react to excessive temperature in the same way electrical fuses react to excessive current.
What Is Thermal Fuses
Thermal fuses are simple but crucial safety devices used in various appliances and electronics. They are a tiny and temperature-sensitive device which interrupts an electrical circuit under a high-temperature condition.

Benefits of Thermal Fuses
-
Simple and Reliable: They offer a straightforward and dependable way to safeguard against overheating.
-
One-Time Cut-Off: The single-use nature ensures a complete power cut in case of severe overheating, preventing further damage.
-
Cost-Effective: They are relatively inexpensive components to incorporate into a device.
Types Of Thermal Fuses
Thermal fuses come in various types, each with its own characteristics and ideal applications.
-
One-Time Use (Disposable)
These are the most common type. Once triggered by heat, they permanently sever the circuit and need replacement. They offer a simple and reliable failsafe for overheating. (Examples: Coffee makers, hair dryers)

-
Resettable
These thermal fuses can automatically reset after the temperature cools down. They are less common but may be used in specific applications where resetting is desirable.
-
Disc-Based
These fuses contain a heat-sensitive disc that melts or warps when triggered, interrupting the circuit.
-
Glass Tube
A glass tube encloses a meltable alloy or a spring mechanism that separates upon reaching the trigger temperature.

-
Surface-Mount
These compact fuses are suitable for use on printed circuit boards (PCBs) in electronic devices.

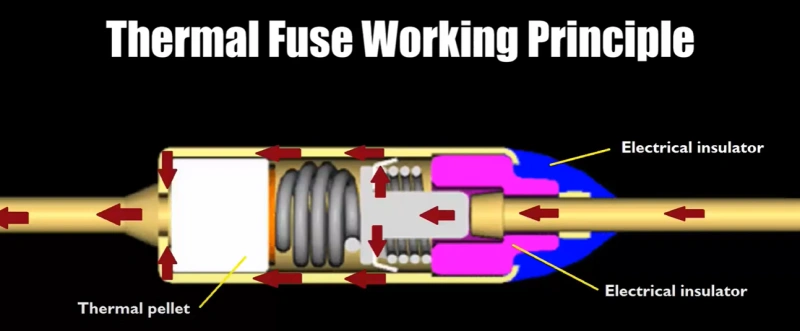
How Does A Thermal Fuse Work
Thermal fuses are the electrical circuit equivalent of fire alarms. They act as silent guardians, constantly monitoring the temperature around them and severing the electrical connection if things get too hot.
A Heat-Sensitive Material Functions:
-
Special Wax: Melts at a specific temperature.
-
Meltable Alloy: A metal compound that liquefies when it gets too hot.
When everything is functioning normally, electrical current flows freely through the fuse without affecting the heat-sensitive material. The temperature surrounding the fuse stays within its designated operating range.
If the temperature around the fuse rises above its specified rating due to a malfunction or overload, here's what happens:
-
Heat Transfer: The surrounding heat conducts to the thermal fuse.
-
Trigger Point Reached: As the temperature increases, it eventually reaches the threshold for the heat-sensitive material.
-
Material Reacts:
-
Wax: The wax melts, losing its structural integrity and breaking the internal electrical connection.
-
Meltable Alloy: The alloy liquefies, similar to the wax, disrupting the current flow path.
A One-Time Sacrifice:
Unlike a circuit breaker that can be reset, thermal fuses are designed for single use. Once triggered, they permanently cut the circuit and require replacement. This ensures a complete power cut-off in case of severe overheating, preventing further damage and potential fire hazards.
How To Install Thermal Fuse
Installing a thermal fuse requires some caution and technical know-how.
-
Identify the Faulty Fuse
Consult your appliance's manual or service guide to locate the thermal fuse. It might be near the heating element, motor, or transformer (depending on the appliance).
-
Access the Fuse
You'll likely need to disassemble part of the appliance to reach the fuse. This could involve removing screws on the back panel or underneath the appliance.
-
Remove the Old Fuse
Once you've located the fuse, note how it's connected in the circuit. You might need to desolder the connections or use wire cutters to snip the leads (depending on the type of fuse).
-
Install the New Fuse
Ensure the new fuse matches the specifications (trigger temperature and current rating) of the original one. Solder the new fuse into place if required, or carefully insert the leads into the designated connection points. Double-check the polarity if applicable.
-
Reassemble the Appliance
Carefully put everything back together, ensuring all screws and connections are secure.
Conclusion
In essence, thermal fuses are simple yet crucial safety devices. Their self-sacrificing nature ensures a complete shutdown in case of overheating, safeguarding appliances and electronics from potential damage.

Disclaimer: The views and opinions expressed by individual authors or forum participants on this website do not represent the views and opinions of Chipsmall, nor do they represent Chipsmall's official policy.

share this blog to: