OUTLINE:
Touch Me Not: The Rise of Fingerprint Scanning
 206
206If you've ever watched a crime scene investigation show, you know how important fingerprints can be in solving a case. 
Fingerprint sensors, however, are much more than just a tool for catching criminals. They're also an everyday part of our lives, used to secure access to our phones, computers, and even our homes.
What are fingerprint sensors?
Fingerprint sensors are electronic devices that can capture and recognize a person's unique fingerprint pattern for authentication and identification purposes. These sensors typically use either capacitive or optical technology to detect the ridges and valleys of a person's fingerprint, which are then compared to a stored database of fingerprints to verify the identity of the person.
✅Let's take a closer look at the different types of fingerprint sensor technologies and how they work.
- Optical fingerprint sensors: They use optical imaging technology to capture and digitize an individual's finger image. The process involves placing the finger on a glass surface of an optical scanner, where illuminating light beams create an impression of both ridges and valleys. The reflections are collected by a lens before being focused onto a CCD or CMOS camera that captures the fingerprint, which is then transformed into a digital image by an A/D converter.
- The technology offers many advantages, including speed, high accuracy, and low power consumption. Optical fingerprint sensors are also easy to integrate into existing systems and are cost-effective.
- However, there are some limitations to optical fingerprint sensors. The sensors can be affected by environmental factors such as dirt, dust, and moisture, which can affect the quality of the captured fingerprint image. Additionally, optical fingerprint sensors can be less reliable than other types of sensors, especially in cases where the finger is scarred or wrinkled.

- Capacitive fingerprint sensors: These sensors generate an electric field that detects changes in capacitance as the finger or other conductive object passes over it. The conductive elements in the sensors are made up of tiny capacitors, which can detect small changes in electric fields caused by the presence of the finger.
- The readout circuitry then measures the change in capacitance and converts it into a digital signal using an analog-to-digital converter (ADC). The controller then processes this signal to extract features such as ridge width, ridge angle, and overall shape. This information is then used to create a fingerprint template, which is compared against other templates stored in the database.
- Finally, a matching score is assigned to determine if the individual is authenticated or not. Capacitive fingerprint sensors offer a fast and reliable way of authentication, as the process can be completed in just a few seconds. However, these sensors also have certain limitations, such as vulnerability to dirt, moisture, and damage to the finger's surface, which can affect the quality of the captured fingerprint image.

- Ultrasonic fingerprint sensors: These scanners send pulses of ultrasonic sound waves from the transducer to the finger being scanned. The sound waves echo back off of the fingerprints' ridges and sweat pores and are collected by the receiving transducer. This echo is then converted into digital format and stored as a template for future comparison.
- Ultrasonic fingerprint scanning offers several advantages, such as the ability to capture a 3D image of the fingerprints, making it easier to distinguish between fingerprints even when they are dirty or have oil on them. The technology is also more reliable than other fingerprint scanning technologies, especially when the finger is dry or cold.

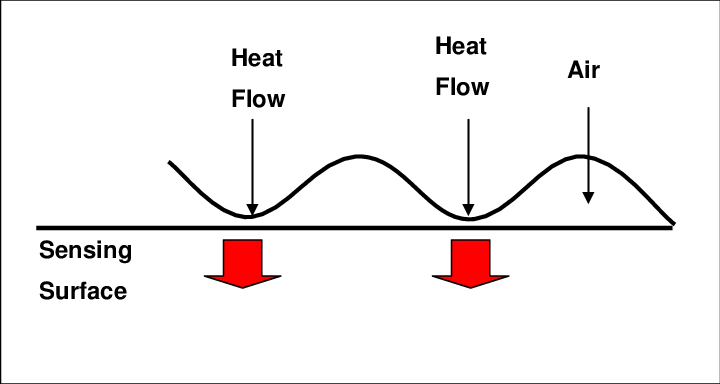
- Thermal fingerprint sensors: These sensors use thermal imaging technology to measure the amount of heat generated by a finger when it is placed on the scanner. The sensor detects any temperature variation between the ridges and valleys of the fingerprint against normal air temperatures using pyro-electric material, and transistors generate an electric charge that forms a distinct digital template for authentication purposes.
- Thermal fingerprint scanners require the user to swipe their finger at a certain speed and angle for an accurate reading. Once the scanning is complete, the system compares the finger-scanning data to the template stored on the secure database for authentication.
Fingerprint sensors have revolutionized the security industry by providing a fast and reliable method of authentication. Each fingerprint sensor technology has its own strengths and limitations, and the choice of technology ultimately depends on the specific needs of the application. We hope this overview has been informative and helpful in understanding the different types of fingerprint sensor technologies available in the market.

Disclaimer: The views and opinions expressed by individual authors or forum participants on this website do not represent the views and opinions of Chipsmall, nor do they represent Chipsmall's official policy.

share this blog to:

