OUTLINE:
Different Types of 3D Printer Filament: Basic Guides
 447
447Welcome to the world of 3D printing filaments. With each layer, new options open up. These flexible materials, like PLA's ability to be eco-friendly, ABS's ability to be tough, and PETG's ability to bend, are what make additive manufacturing new. For making prototypes or strong parts, each type of 3d printer filament has the perks that make it easier and more precise for creators to bring their ideas to life. Come with us as we explore the different types of 3D printer filaments and many ways these materials can be used to turn ideas into real things, one print at a time.

What are 3D Printing Filaments
3D printing filaments are made of thermoplastic materials. Filaments are spools of materials that are heated, melted and pushed through a 3D printer's tip one layer at a time to make the shape you want. The filament you pick will directly impact the outcome of your print, including its quality, longevity, and usefulness. Because filaments are made of various materials and come in various colors and sizes, they can be utilized for various tasks, ranging from creating basic models to creating intricate machine parts.
A filament's evenness, melting point, and tensile strength are very important for the printing process and how well the end product works. Three-dimensional printing filaments have changed design, prototyping, and manufacturing. They make it simple to create useful and complex objects in a way that is adaptable, customized, and cheap.
Different Types of 3D Printer Filament
Here are the following 12 types of 3d printer filament:
PLA
Polylactic Acid (PLA) is a bio-based material that comes from cornstarch or sugarcane, which can be grown again and again. PLA is popular because it is easy to work with, breaks down naturally, and comes in a lot of bright colors, from soft pastels to bright primary colors. It is a great choice for beginners because it is flexible, has a low printing temperature, and doesn't tend to warp much, making printing go more smoothly. PLA prints have a glossy finish that makes them look better, and they can be used for many things, from fast prototyping to making intricate art. This shows how flexible and adaptable PLA is in the world of 3D printing.
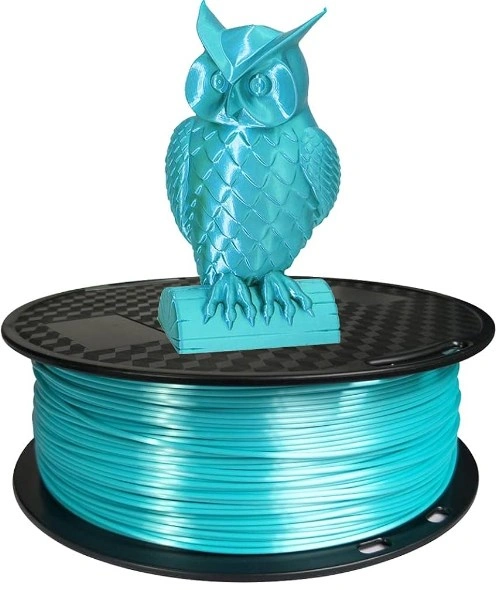

Image Source: Amazon
ABS
Due to its excellent mechanical qualities, Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) is a long-lasting thermoplastic that is widely used in manufacturing. As a result of its high strength and resistance to impact, ABS is commonly used to make functional parts for things like electronics, consumer goods, and car parts. Its toughness makes it perfect for uses that need long-lasting and dependable materials. Although ABS doesn't need a hot print bed to keep it from warping during printing, it does give off fumes that need to be properly vented for safe use. For easy post-processing of ABS prints, they can be improved by sanding and painting to get the look and function you want.

Image Source: Matterhackers
PETG
Polyethylene Terephthalate Glycol-Modified (PETG) is strong like ABS but easy to print on like PLA. It's very strong, flexible, and doesn't react badly with water or chemicals, so it can be used for mechanical parts and containers that need to work reliably in tough circumstances. PETG prints at slightly higher temperatures than PLA, but it doesn't warp much and the layers stick together well, so the results are the same for both working prototypes and parts that will be used in real life.
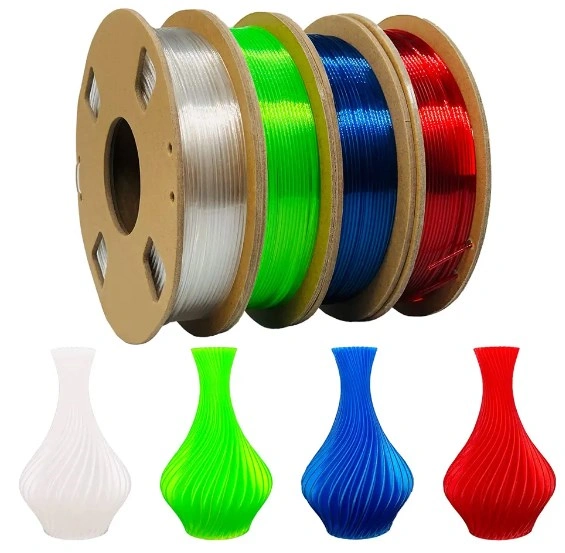

Image Source: Torwell
TPU
Thermoplastic Polyurethane (TPU) is a flexible filament that works great for printing seals, gaskets, and unique shoes that have elastic parts. TPU is resistant to wear and can be stretched many times without losing its shape, so it can be used in places where impact absorption and durability are needed. Because it is flexible, it needs a direct drive printer and can be printed at slower speeds to ensure quality and accuracy in size and shape. This makes sure that flexible printed parts last and work well.
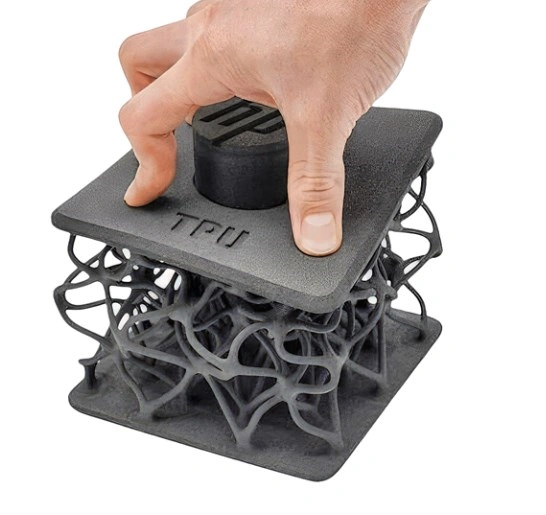

Image Source: facfox3d
Nylon
Nylon is a flexible thermoplastic that is strong, long-lasting and doesn't wear down easily. This makes it perfect for useful parts like gears, bearings, and structural parts in tough engineering situations. Nylon takes in water from the air, which lowers the quality of prints, so it needs to be stored carefully and may need to be dried before use to keep working at its best. Nylon is tough and has a low friction coefficient, which makes it good for uses that need to be resistant to pressure and flexible. It works well in many industrial settings.
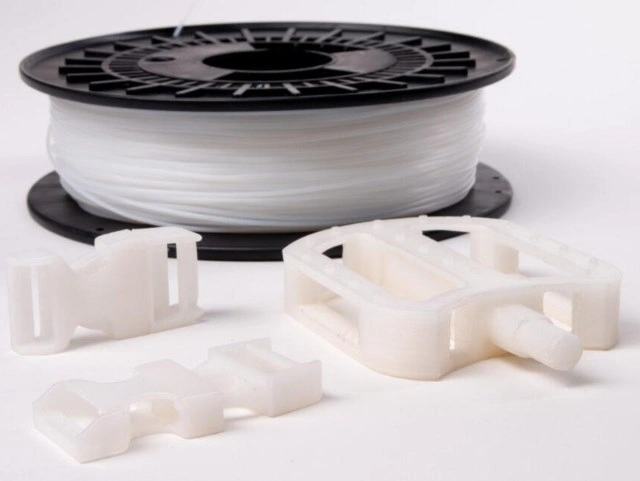

Image Source: ZMorph
PVA
PVA (Polyvinyl Alcohol) is a water-soluble thread that is used as support material in 3D printers with two extruders. Since it breaks down in water, it's easy to get off of complicated prints without hurting the model. PLA and other materials that don't need to be printed at high temperatures can be used with PVA. But PVA doesn't like water and needs to be kept in airtight cases to keep its print quality. This makes it a great choice for complicated prints that need support inside and lots of small details.

Image Source: MatterHackers
HIPS
High-impact polystyrene (HIPS) is a lot like ABS, but it dissolves in limonene. This makes it a great material for support structures in ABS prints and other projects that need strong support. HIPS is strong, doesn't weigh much, and is easy to finish by sanding, gluing, or painting, so you can choose from a variety of choices. It gives off fumes like ABS when it's printed, so make sure there is enough airflow for safe use and make sure it works with 3D printers that have two extruders.

Image Source: 3Dnatives
ASA
Acrylonitrile Styrene Acrylate (ASA) is a material that is stable in UV light and better at withstanding weather. This makes it good for outdoor uses that need to last and keep their color over time when exposed to direct sunlight. ASA prints similarly to ABS, but it works better outside, where it needs a hot print bed and good airflow because it gives off emissions while printing. It's used for useful parts and prototypes that need to last a long time and look good in a variety of environments.

Image Source: ZMorph
Carbon Fiber
Carbon Fiber filament mixes PLA or ABS with chopped carbon fibers to make printed parts stiffer, stronger, and more stable in their shape. It is used in industries like aerospace, automotive, and robotics that need high-performance, lightweight structural parts. Carbon Fiber fiber is rough on 3D printer nozzles, so they need to be maintained regularly or hardened for long-term use. It makes prints with a matte finish and a unique fiber texture that are great for situations where strength and stiffness are very important.

Image Source: Jawstec
Metal Filaments
The incorporation of metal powders, such as brass, copper, or stainless steel, into a PLA or ABS matrix results in the production of prints that have a metallic appearance and weight, making them appropriate for use in the prototyping of metal components or for decorative purposes. When printing with metal filaments, it may be necessary to use specialist nozzles and settings. Additionally, post-processing processes like as polishing or patination may be necessary to get the ideal aesthetics. This will ensure that metallic-like finishes are accurate and detailed.

Image Source: MatterHackers
Wood Filament
Wood Filament combines PLA with recycled wood fibers to make prints that look and feel like real wood. These prints are great for artistic and decorative uses like making furniture prototypes, sculptures, and building models. Due to the rough nature of wood fibers, wood filament needs larger diameter needles. Post-processing methods like sanding, staining, or varnishing can be used to improve the wood grain effect, giving you more options for making prints that look good and have natural textures.
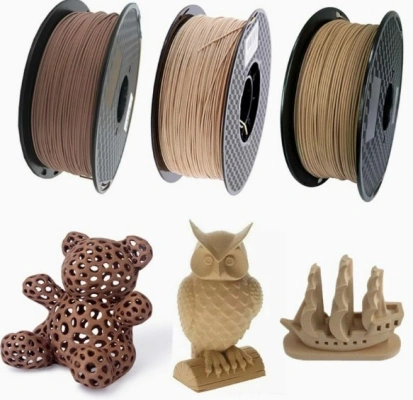

Image Source: eBay
Glass Fiber
Glass Fiber thread is made up of broken glass fibers that are mixed with a polymer. When you print something, it gets stiffer, and stronger, and keeps its shape better. This is important for mechanical parts that need to work well and not break easily. It can be used for jobs that need strong structure and can handle heat. The prints it makes have a matte finish. But because glass fibers are rough, 3D printer nozzles need to be cleaned and fixed often to get uniform, good results.
There are different kinds of thread, and each one is good for different things. Because of this, 3D printing technology is very adaptable and fluid.
Image Source: TCT Magazine
Which Filament is Best for 3D Printing
Your project needs will play a big role in picking the "best" fiber for 3D printing. Polylactic Acid (PLA) is easy to use and is often recommended for printing that needs to be done in different ways. It's also biodegradable, comes in a lot of colors, and needs lower printing temperatures, so it can be used for both easy and complicated patterns.
When durability and resistance to impact are important, ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene) is often chosen, even though it needs a hot print bed and airflow because it emits fumes. PETG (Polyethylene Terephthalate Glycol-Modified) is also stronger than ABS and can handle chemicals, which makes it a good material for making useful parts.
Thermal Plastic Polyurethane (TPU) is good for certain uses, like being flexible, and Polyvinyl Alcohol (PVA) is a base material that dissolves in water and can be used for complex prints. The best filament to use will depend on the quality of the print you want, its mechanical features, how it will affect the environment, and the post-processing needs of your project.
Filament FAQ
What is the difference between PLA and ABS filaments
Polylactic Acid (PLA) and Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) are two popular 3D printing filaments that are different from one another. PLA comes from naturally occurring materials, breaks down naturally, is easy to print, and doesn't bend much. ABS is stronger and less likely to break when it hits something, but it gives off fumes and needs a hot print bed.
How do you store filament to prevent moisture absorption
Filaments like Nylon and PVA take in water from the air, which lowers the quality of the print. Keep them dry by putting them in airtight cases with desiccants like silica gel. PLA, ABS, and PETG are less sensitive, but they do better when stored in a cool, dry place with a lid.
Can you mix different filaments in one print
Using suitable printers, you can mix filaments like PLA and PVA to make supports or prints with two layers. To print well, make sure that both fibers have the same temperature and stick together well.
What are the best settings for printing flexible TPU filaments
To keep the printer from getting clogged, printing TPU (Thermoplastic Polyurethane) needs a direct drive extruder, slower print speeds, and lower retraction settings. A warm bed is not necessary, but it does help with sticking.
How do you recycle used filament spools
A lot of places that recycle will take empty plastic thread spools. Before you recycle them, make sure they are clean and free of any dust. Some companies offer recycling services for their spools to help the environment.
Where can I Buy a 3D Printer Filament
You can buy filament for 3D printers from several online shops and stores that specialize in them. Filaments like PLA, ABS, PETG, and more can be bought on sites like Chipsmall. It's easy to find the right filament for your 3D printing needs on Chipsmall because it has competitive prices, full product descriptions, and customer reviews. They make sure the quality is good and reliable, and they can help both new and experienced users who are looking for certain colors or materials. To make sure you have a smooth buying experience for your next printing job, check their website for deals, bulk discounts, and shipping options.
Conclusion
3D printer filaments come in a lot of different types that can be used for a lot of different things. Each type of 3d printer filament material has its benefits for different printing projects. For example, PLA is good for the environment and easy to use, while ABS and PETG last longer and are resistant to chemicals. Specialized materials, such as TPU for flexibility and PVA for support that dissolves, make 3D printing filaments even more flexible. Whether you're an artist exploring new creations or an engineer prototyping useful parts, knowing the features and benefits of each filament type lets you make smart decisions that improve print quality and performance.

Disclaimer: The views and opinions expressed by individual authors or forum participants on this website do not represent the views and opinions of Chipsmall, nor do they represent Chipsmall's official policy.

share this blog to:

