OUTLINE:
Types of Resistors
 584
584Resistors are electronic components that limit or resist the flow of electrical current through a circuit. There are several types of resistors commonly used in electronic circuits, each with their specific features.
Carbon Composition Resistor: This is one of the oldest and most common types of resistors. It is made of carbon particles mixed with a binder material and molded into the desired shape. They have high noise and temperature coefficients and are not suitable for high-frequency applications. Commonly used in low-power circuits, with poor durability and temperature stability.
.jpg)
Metal Film Resistor: This type of resistor is made of a metal film deposited onto a ceramic substrate. Metal film resistors have better accuracy and stability than carbon film resistors and can handle higher power ratings.
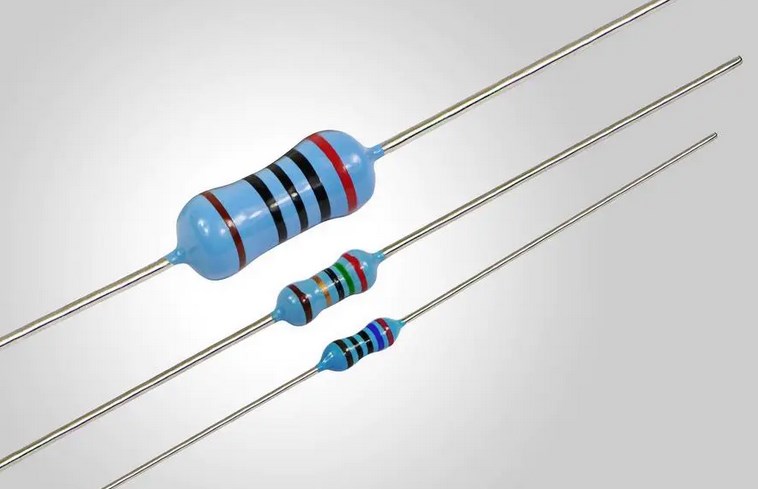

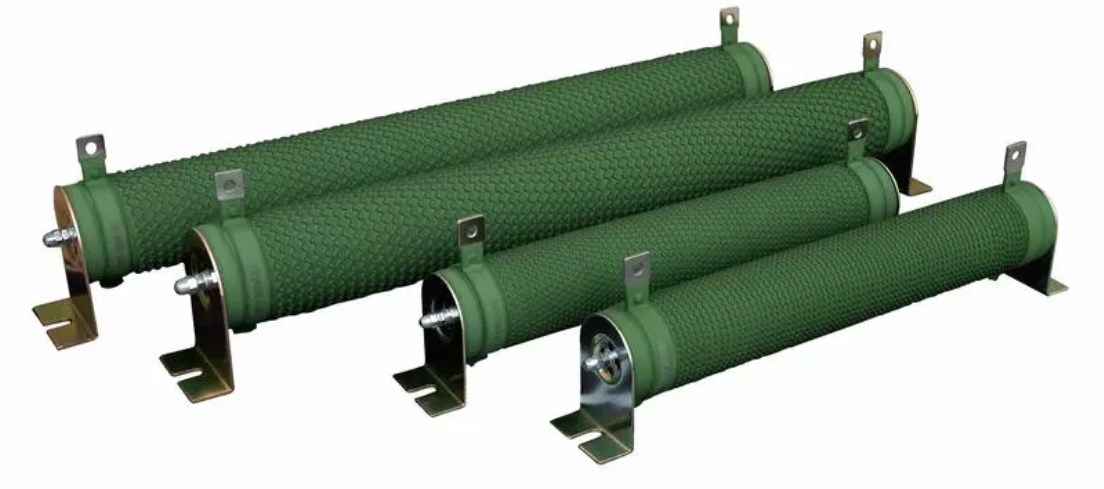
Wirewound Resistor: A wirewound resistor is made by winding a metal wire around an insulating core. They are highly accurate and stable but are relatively expensive. Wirewound resistors are used in high-power applications.

Thick Film Resistor: Thick film resistors are made by depositing a thick layer of conductive material on a ceramic substrate. They offer excellent stability and precision and are used in temperature-sensitive applications.

Surface Mount Resistor: Surface mount resistors (SMDs) are tiny resistors that can be mounted directly on the surface of a printed circuit board. They are commonly used in electronic devices where space is limited.
Metal Oxide Film Resistor: Metal oxide film resistors are similar to film resistors, except they have a thin layer of metal oxide deposited on the ceramic substrate. They have a low temperature coefficient and are more stable than carbon composition resistors.

Variable Resistor: A variable resistor, also known as a potentiometer, is a resistor that allows the resistance value to be adjusted manually. They are often used for tuning circuits or adjusting the volume of audio equipment.


Disclaimer: The views and opinions expressed by individual authors or forum participants on this website do not represent the views and opinions of Chipsmall, nor do they represent Chipsmall's official policy.

share this blog to:

