OUTLINE:
What Is Ultrasonic Wire Splice And How Does It Work
 316
316In today's rapidly advancing industries, efficient wire splicing techniques are crucial for seamless connectivity. Ultrasonic wire splicing is a fascinating technology that revolutionized cable and wire joining. Let's explore what an ultrasonic wire splice is and how it revolutionizes wire splicing in various sectors.
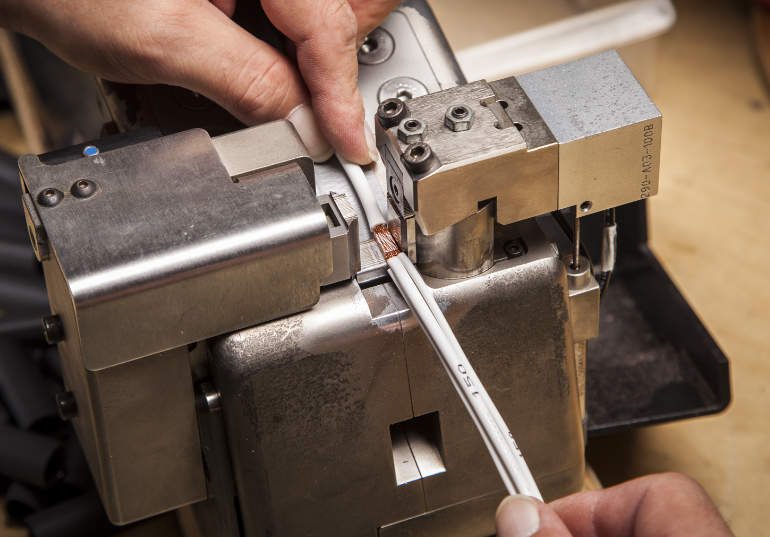

Question 1: What Is Ultrasonic Wire Splice
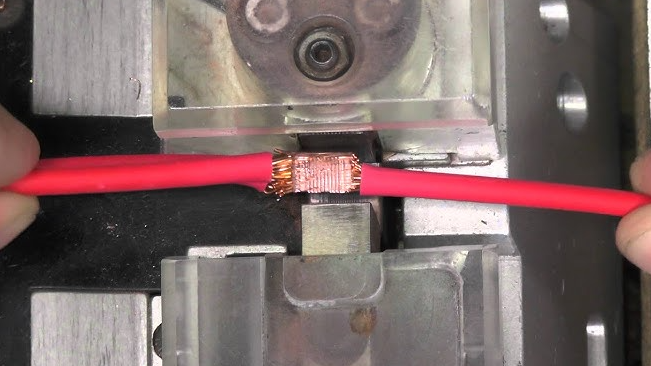
Ultrasonic wire splice employing high-frequency vibrations, permanently connects the ends of two or more wires, resulting in a strong and electrically conductive bond. Unlike traditional processes like soldering or crimping, this technology forgoes the need for heat or other materials. The process involves joining multiple wires with each other or joining wires with terminals or conductive contacts.
Question 2: How Does Ultrasonic Wire Splicer Work
The ultrasonic wire splicing machine performs the following steps:
- Preparation: The wires to be spliced are stripped of insulation at the ends, exposing the bare metal conductors.
- Clamping: The prepared wire ends are securely clamped or kept in place using the ultrasonic wire splicer's equipment.
- Ultrasonic Welding: The ultrasonic wire splicer produces ultrasonic vibrations, which typically range in frequency from 20 to 70 kHz. These vibrations are applied to the wires' connection points. The vibrations generate friction and heat at the wires' contact points, forcing them to melt and fuse together.
- Cooling: After ultrasonic welding, the molten wire connection is allowed to cool and solidify, resulting in a strong and lasting bond.
Question 3: How Strong Is Ultrasonic Welding
Ultrasonic wire splice is a non-contact, solid-state welding technology that employs high-frequency vibrations (ultrasonic waves) to form a strong and dependable bond between two or more wires without the need of solder or other materials such as adhesives.
When conducted correctly, ultrasonic welding can produce welds with equivalent strength to the parent materials. The method includes applying high-frequency vibrations to the components being welded, which generates localized heat and causes the material to melt and join together. The resulting weld is often free of voids, porosity, and other flaws, resulting in a strong and reliable bond.
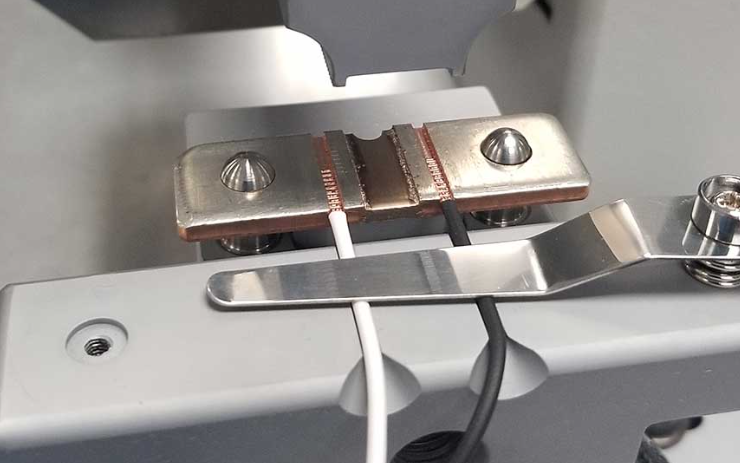

Question 4: The Advantages of Ultrasonic Welding
Ultrasonic welding is a versatile technique used in various industries for joining plastic components, such as automotive parts, electronic enclosures, medical devices, and packaging materials. It offers several advantages over traditional bonding methods like soldering:
Speed and Efficiency: Ultrasonic welding is a rapid process that can create strong bonds within seconds, making it highly efficient for high-volume production lines. The fast cycle times contribute to increased productivity and reduced manufacturing costs.
No Additional Materials: Unlike soldering, ultrasonic welding does not require additional materials like solder or adhesives. It relies solely on the mechanical vibrations and heat generated during the process to create the bond. This eliminates the need for consumables and simplifies the production process.
Clean and Environmentally Friendly: Ultrasonic welding is a clean process since it doesn't involve the use of flux or flux residues like soldering. It produces no smoke, fumes, or toxic byproducts, making it environmentally friendly and suitable for applications with strict regulatory requirements.
Consistent and Repeatable Results: Ultrasonic welding offers excellent repeatability, ensuring consistent bond strength and quality across multiple production runs. The parameters, such as vibration frequency, amplitude, and welding time, can be precisely controlled, resulting in reliable and uniform welds.
Hermetic Sealing Capability: Ultrasonic welding can create hermetic seals, particularly in plastic components used in the automotive and medical industries. The strong bond formed by ultrasonic welding prevents the ingress of moisture, gases, or other contaminants, ensuring the integrity and longevity of the sealed products.
Design Flexibility: Ultrasonic welding allows for flexibility in design and joint configurations. It is compatible with complex geometries, including joints with varying thicknesses or hard-to-reach areas. This versatility enables engineers to explore innovative designs without compromising the integrity of the weld.
Question 5: The Difference Between Ultrasonic Welding and Soldering
Ultrasonic welding and soldering are two independent procedures for joining materials that differ in their principles, applications, and the type of bonds they form.
Principle:
Ultrasonic Welding: Ultrasonic welding uses high-frequency mechanical vibrations to generate heat and create a bond between materials. The friction and pressure generated by the vibrations cause the materials to melt and fuse together.
Soldering: Soldering involves melting a filler material called solder, typically a metal alloy, which flows into the joint between the materials being joined. The solder solidifies upon cooling, forming a bond between the materials.
Materials:
Ultrasonic Welding: Ultrasonic welding is commonly used for joining thermoplastic materials, such as plastics. It can also be used for some non-ferrous metals.
Soldering: Soldering is primarily used for joining metals and electronic components, such as circuit boards. It is not suitable for joining thermoplastic materials.
Bond Strength:
Ultrasonic Welding: Ultrasonic welding forms a strong link between materials, generally comparable in strength to the parent materials. Factors influencing bond strength include welding conditions, material compatibility, and joint design.
Soldering: The strength of soldered junctions is determined by the type of solder used and the effectiveness of the soldering process. While soldered junctions might be mechanically strong, they are typically not as strong as their parent materials.
Applications:
Ultrasonic Welding: Ultrasonic welding is commonly used in industries such as automotive, electronics, medical devices, and packaging for joining plastic components.
Soldering: Soldering is widely used in electronics manufacturing, including circuit board assembly, component soldering, and wire connections.
Tips: Chipsmall - We Provide The Cheapest Wire You Are Looking for
Speaking of joining materials, if you are in need of affordable wire for your projects, we have great news: we provide the cheapest wire you are looking for.
Chipsmall Limited consists of a professional team with an average of over 20 years of expertise in the distribution of electronic components. Main products comprise ICs, resistors, capacitors, modules, potentiometers, IC sockets, relays, connectors and so on.
Wrap Up
Ultrasonic wire splicing has become a standard technique in various industries due to its speed, reliability, and clean execution. Utilizing an ultrasonic wire splice technology to enable precise and reliable wire connections, whether it's joining multiple wires together or attaching wires to terminals or conductive contacts. It makes a significant contribution to various industries thanks to its unique approach and superior joint quality.

Disclaimer: The views and opinions expressed by individual authors or forum participants on this website do not represent the views and opinions of Chipsmall, nor do they represent Chipsmall's official policy.

share this blog to:

