OUTLINE:
Understanding PIR Sensors
 290
290PIR (Passive Infrared) sensors are widely used electronic devices that enable motion detection by detecting changes in infrared radiation within their surroundings. They have become an integral part of security systems, automatic lighting systems, and various other applications where the detection of human or animal movement is essential. This article explores the working principle of PIR sensors, their components, and their applications in greater detail.
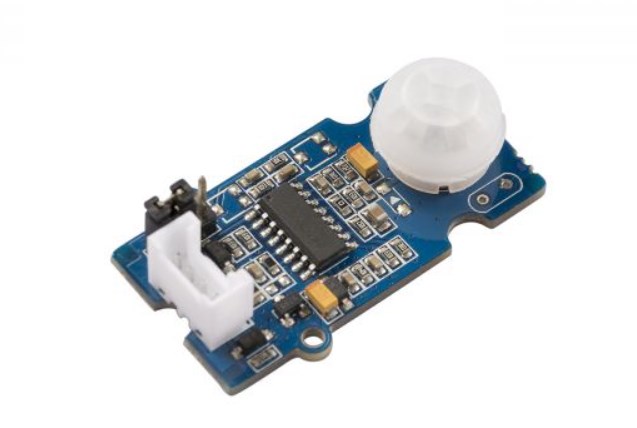

Working Principle:
At the core of a PIR sensor lies a pyroelectric material, typically a crystalline substance with pyroelectric properties. This material generates an electric charge when subjected to rapid temperature changes. The PIR sensor incorporates multiple segments of this pyroelectric material, each connected to an electrode. Additionally, a lens is employed to focus infrared energy onto these segments.
When there is no movement within the sensor's range, the temperature across all segments remains constant, resulting in no net change in electric charge. However, when a warm object, such as a human or animal, moves within the sensor's field of view, it alters the infrared radiation pattern falling on the segments.
The PIR sensor utilizes a differential detection principle. It compares the infrared radiation levels between adjacent segments. As an object moves, the temperature change between adjacent segments becomes unequal, leading to a net difference in the electric charge across the electrodes. This change is converted into a voltage signal by the sensor's electronics.
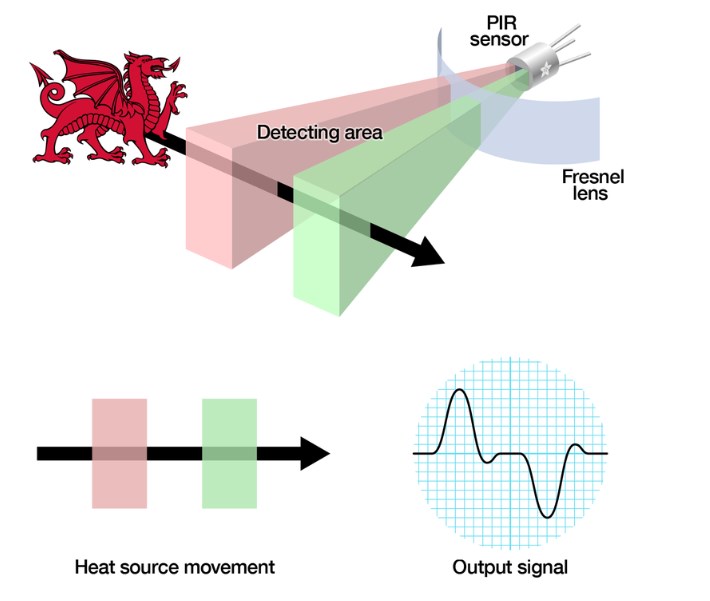
Signal Processing and Output:
The voltage signal generated by the pyroelectric material is amplified and processed to determine the presence of motion. Through appropriate circuitry, the processed signal is compared to a predefined threshold. If the signal exceeds this threshold, motion is detected, and the PIR sensor sends a signal to an associated circuit or device.
Applications of PIR Sensors:
Security Systems: PIR sensors are extensively used in security systems to detect intruders. When combined with alarm systems, they can trigger alerts or activate sirens, notifying occupants or security personnel.
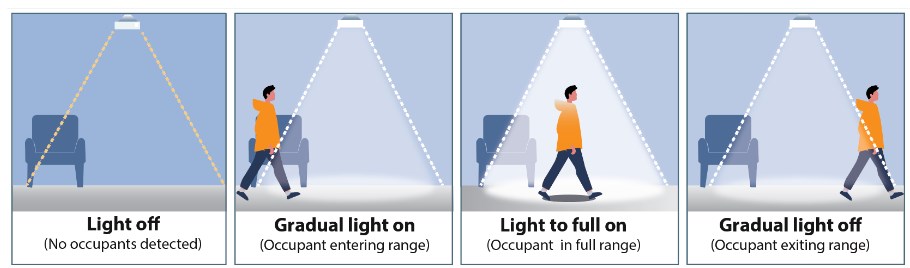
Lighting Systems: PIR sensors are commonly employed in automatic lighting systems. By detecting motion, they can switch on lights when someone enters a room and turn them off when there is no movement, thus conserving energy.
Home Automation: PIR sensors play a crucial role in home automation, enabling various smart functionalities. They can initiate actions like adjusting temperature settings, activating surveillance cameras, or controlling multimedia systems based on detected motion.
Occupancy Sensing: PIR sensors find utility in occupancy sensing applications. They can determine if a space is occupied and, based on that information, regulate heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems to optimize energy usage.
Retail Analytics: In commercial environments, PIR sensors are utilized for retail analytics. By tracking customer movement and behavior, they provide insights into customer flow, allowing businesses to optimize store layouts and improve customer experiences.
PIR sensors are passive electronic devices that detect changes in infrared radiation emitted by objects within their field of view. By converting these changes into electrical signals, they enable reliable motion detection. With applications ranging from security systems to automatic lighting and home automation, PIR sensors have become indispensable in numerous fields. Their ability to detect human and animal movement with high precision makes them a valuable component in enhancing safety, security, and energy efficiency in various environments.

Disclaimer: The views and opinions expressed by individual authors or forum participants on this website do not represent the views and opinions of Chipsmall, nor do they represent Chipsmall's official policy.

share this blog to:

