OUTLINE:
An Introduction for V-Regulator: Types&Working Principles
 234
234Ever wondered how your devices maintain stable power, even amidst fluctuations?
Step into the realm of voltage regulators, where stability is not just a concept but a guarantee. Explore the diverse types and core principles guiding these essential components.
Image Source:https://www.sparkfun.com/products/12766
From linear to switching regulators, unravel the backbone of stable voltage in electronic circuits. Ready to unlock the secrets behind seamless power delivery?
This journey through fundamentals empowers you to navigate the intricate landscape of electronics with confidence.
What Is the V-Regulator[Definition]
A voltage regulator, often abbreviated as V-regulator, is an electronic component or circuit that maintains a stable output voltage regardless of changes in input voltage or load conditions.
Its primary function is to ensure that the voltage supplied to a device or circuit remains within a specified range, providing a consistent and reliable power supply.
Voltage regulators are essential in various electronic applications where stable voltage is crucial for proper operation.
They are commonly used in power supplies, battery charging circuits, voltage references, and voltage stabilization circuits.
How Does A V-Regulator Work
Here's a step-by-step explanation of how a voltage regulator works:
Input Voltage Regulation:
The voltage regulator receives an input voltage from a power source, such as a battery or an AC adapter. This input voltage may fluctuate due to changes in the power source or variations in the load.
Error Detection:
The voltage regulator compares the input voltage with a reference voltage. If there is a difference between the input voltage and the reference voltage, an error signal is generated.
Control Circuitry:
The error signal is processed by the control circuitry of the voltage regulator. This circuitry determines the required adjustment to the output voltage based on the error signal.
Adjustment of Output Voltage:
The control circuitry adjusts the output voltage of the regulator to compensate for any deviations from the desired voltage level. This adjustment is typically achieved by controlling the flow of current through the regulator circuit.
Voltage Regulation:
The voltage regulator maintains a stable output voltage by continuously monitoring the input voltage and making real-time adjustments to the output voltage as needed. This ensures that the output voltage remains within a specified range, regardless of changes in the input voltage or load conditions.
Feedback Loop:
The voltage regulator operates in a closed-loop feedback system, where the output voltage is constantly compared to the reference voltage. Any deviations from the reference voltage are detected and corrected by the control circuitry, ensuring precise voltage regulation.
Load Regulation:
In addition to regulating the input voltage, the voltage regulator also adjusts the output voltage to compensate for changes in the load. This ensures that the output voltage remains stable even when the connected devices draw varying amounts of current.
Various Types of V-Regulator in 2024
As of 2024, there are various types of voltage regulators available, each designed for specific applications and requirements.
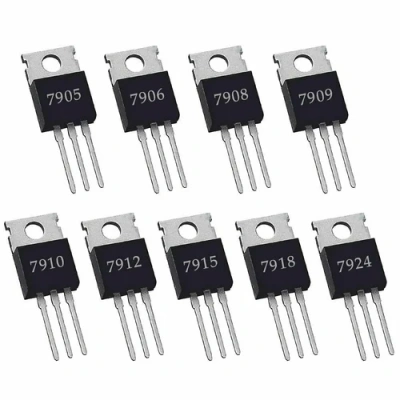

Image Source: IndiaMART
Here are some common types, including the ones you mentioned:
7905, 7906, 7908, 7909, 7910 Series (Negative Linear Voltage Regulators):
These are part of the 79xx series of linear voltage regulators, which provide a stable negative output voltage. Each regulator in this series has a fixed output voltage, such as -5V (7905), -6V (7906), -8V (7908), -9V (7909), and -10V (7910). They are widely used in applications where a stable negative voltage supply is required, such as in amplifiers, power supplies, and industrial control systems.
LM78xx Series (Positive Linear Voltage Regulators):
Similar to the 79xx series, the LM78xx series consists of positive linear voltage regulators that provide a stable positive output voltage. They are available with various fixed output voltages, such as +5V (LM7805), +6V (LM7806), +8V (LM7808), +9V (LM7809), and +10V (LM7810). These regulators are commonly used in a wide range of electronic devices and circuits to provide a regulated power supply.
LM317 (Adjustable Linear Voltage Regulator):
The LM317 is a popular adjustable linear voltage regulator that allows users to set the output voltage to a desired level within a specified range. It is widely used in applications where a variable output voltage is required, such as in laboratory power supplies, battery chargers, and voltage references.
LM2940 (Low Dropout Regulator):
The LM2940 is a low dropout voltage regulator designed to provide a stable output voltage with minimal dropout voltage (the minimum voltage difference between the input and output). It is suitable for applications where the input voltage may be close to the desired output voltage, such as in battery-powered devices and automotive electronics.
LM2576 (Switching Voltage Regulator):
The LM2576 is a switching voltage regulator that offers high efficiency and low heat dissipation compared to linear regulators. It is commonly used in applications where high power efficiency is required, such as in LED lighting, battery charging, and portable electronics.
What Are the Working Principles of V-Regulator
The working principles of a voltage regulator, often referred to as V-regulator, depend on its specific type.
However, the general working principles can be summarized as follows:
Comparison and Error Detection:
The voltage regulator compares the output voltage with a reference voltage. If there's a difference between the actual output voltage and the desired reference voltage, an error signal is generated.
Error Amplification:
The error signal is amplified by an error amplifier within the regulator circuitry. This amplified error signal represents the difference between the actual output voltage and the desired reference voltage.
Control Circuitry:
The amplified error signal is processed by the control circuitry of the voltage regulator. This control circuitry determines the required adjustment to the output voltage based on the error signal.
Feedback Loop:
The voltage regulator operates in a closed-loop feedback system. Any deviation from the desired output voltage results in an error signal, which is fed back to the control circuitry. This feedback loop continuously adjusts the output voltage to minimize the error and maintain stability.
Voltage Adjustment:
The control circuitry adjusts the output voltage of the regulator by controlling the flow of current through the regulator circuit. This adjustment is typically achieved by using semiconductor devices such as transistors or integrated circuits.
Voltage Stabilization:
The voltage regulator stabilizes the output voltage by continuously monitoring the input voltage and making real-time adjustments to the output voltage as needed. This ensures that the output voltage remains within a specified range, regardless of changes in the input voltage or load conditions.
Final Verdict
Delving into voltage regulators unveils a world of essential components vital for stable and reliable power management in electronic circuits.
Understanding their diverse types and intricate working principles provides a foundational understanding crucial for any electronic enthusiast or professional.
From linear to switching regulators, each type serves unique purposes, catering to a wide range of applications with precision and efficiency.
By grasping the fundamental concepts outlined in this introduction, you're equipped to navigate the intricate landscape of voltage regulation, ensuring optimal performance and reliability in your electronic designs and projects.

Disclaimer: The views and opinions expressed by individual authors or forum participants on this website do not represent the views and opinions of Chipsmall, nor do they represent Chipsmall's official policy.

share this blog to:

