OUTLINE:
What Does a Rectifier Do? A Comprehensive Guide
 404
404A rectifier is an essential component in electronics, responsible for converting alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC). This process is crucial in many applications, from power supplies to battery charging systems.What Does a Rectifier Do?Let's examine it and its function in contemporary electronics.

Image Source: Hnhcart
Introduction to Rectifiers
What Does a Rectifier Do?Here is a brief introduction of rectifiers before knowing its functions.
Rectifiers are devices that convert AC, which periodically reverses direction, into DC, which flows in only one direction. This process is known as rectification
The rectification process is essential because it “straightens” the direction of current, allowing for the consistent power supply required by electronic components. Depending on the type of AC supply and the rectifier circuit’s arrangement, the output voltage may need additional smoothing to produce a steady voltage suitable for electronic devices.
The Basic Function of a Rectifier
What does a rectifier do? Rectifiers function by allowing current to flow in only one direction, effectively blocking the reverse current. This process involves several key steps.
1. Converting AC to DC
The primary function of a rectifier is to convert AC to DC. AC voltage, which alternates in polarity, is standard in power outlets. However, electronic devices, such as computers, smartphones, and LED lights, require a steady DC voltage to function correctly. Rectifiers achieve this conversion by allowing current to flow only in one direction.
2. Filtering and Smoothing
After rectification, the DC output still contains ripples (small AC components). To produce a pure DC signal, additional filtering is required. Capacitors and inductors are commonly used to smooth out these ripples, providing a stable DC voltage suitable for sensitive electronic components.
3. Voltage Regulation
In many applications, the rectified and filtered DC voltage must be regulated to a specific value. Voltage regulators are used to maintain a constant output voltage despite variations in the input voltage or load conditions. What does a rectifier do to ensure that electronic devices receive a stable and reliable power supply.
Applications of Rectifiers in Everyday Electronics
Rectifiers are integral to many electronic devices and systems. Here are some common applications.
Power Supplies
Rectifiers are used in power supplies to convert AC from the mains to the required DC voltage for electronic circuits. They ensure that devices receive a stable DC voltage, which is essential for their proper operation.
Radio Signal Detection
In radio receivers, rectifiers demodulate the AC signals to retrieve the audio signals. This process, known as signal detection, is crucial for converting the modulated signal into a usable form.
Battery Charging Systems
Rectifiers are crucial in battery chargers, converting AC to DC to charge batteries efficiently. They ensure that the batteries receive a constant and controlled DC voltage, which is necessary for safe and effective charging.
DC Motor Drives
Many DC motor drives use rectifiers to convert AC to DC, providing the necessary power for motor operation. This application is common in various industries, including automotive and manufacturing.
Electroplating
In electroplating processes, rectifiers provide the DC voltage needed to deposit metals onto surfaces. This application requires precise control of the DC voltage to ensure high-quality plating.
Types of Rectifiers Explained
Understanding the different types of rectifiers can help in selecting the right one for your needs.
Half-Wave Rectifier
The half-wave rectifier uses a single diode and is the simplest form of rectifier. It only allows one half of the AC waveform to pass through, resulting in a pulsating DC. This type is often used in low-power applications where efficiency is not critical.
Full-Wave Rectifier
A full-wave rectifier uses two or more diodes to allow both halves of the AC waveform to pass, producing a smoother DC output compared to a half-wave rectifier. This type is more efficient and is used in applications where a more stable DC output is required.
Bridge Rectifier
A bridge rectifier utilizes four diodes arranged in a bridge configuration. This setup provides full-wave rectification without needing a center-tapped transformer, making it more efficient and versatile. Bridge rectifiers are commonly used in power supplies and other high-efficiency applications.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Different Rectifiers
Each type of rectifier has its own set of pros and cons, which should be considered based on the application.
Half-Wave Rectifier
Advantages: Simple design, low cost.
Disadvantages: Low efficiency, high ripple factor.
Full-Wave Rectifier
Advantages: Higher efficiency, lower ripple factor than half-wave rectifiers.
Disadvantages: Requires more components, potentially higher cost.
Bridge Rectifier
Advantages: High efficiency, no need for a center-tapped transformer.
Disadvantages: More complex design, slightly higher cost due to more diodes.
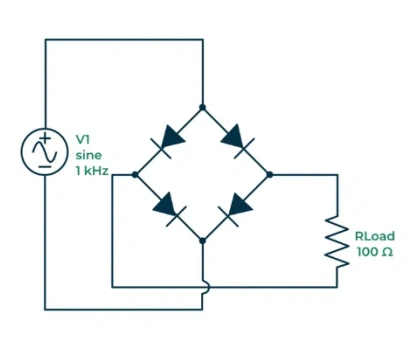
Image Source: GeeksforGeeks
|
Type of Rectifier |
Advantages |
Disadvantages |
|
Half-Wave Rectifier |
Simple design, low cost |
Low efficiency, high ripple factor |
|
Full-Wave Rectifier |
Higher efficiency, lower ripple factor than half-wave rectifiers |
Requires more components, potentially higher cost |
|
Bridge Rectifier |
High efficiency, no need for a center-tapped transformer |
More complex design, slightly higher cost due to more diodes |
How to Choose the Right Rectifier for Your Needs
Selecting the right rectifier involves considering several factors to ensure it meets your specific requirements.
Understanding Your Power Requirements
Determine the voltage and current needs of your application to choose a rectifier that can handle the load. This is crucial for ensuring that the rectifier can provide the necessary power without overheating or failing.
Considering Efficiency and Cost
Balance the efficiency of the rectifier with its cost. More efficient rectifiers may have a higher initial cost but can save money in the long run through reduced energy consumption. For high-efficiency applications, a bridge rectifier might be the best choice.
Evaluating the Load Characteristics
Consider the nature of the load the rectifier will supply. Some loads may require a smoother DC output, influencing the choice of rectifier type. For example, sensitive electronic equipment might benefit from a full-wave or bridge rectifier due to its lower ripple factor.
Recommendation
When choosing a rectifier, it's essential to source from reliable suppliers. Chipsmall is a trusted distributor that offers a wide range of rectifiers and other electronic components. Their extensive inventory and competitive pricing make them an excellent choice for both small-scale projects and large industrial applications.
Final Verdict
Rectifiers play a vital role in converting AC to DC, a process fundamental to the operation of many electronic devices. Understanding what does a rectifier do, knowing the different types of rectifiers, their advantages and disadvantages, and how to choose the right one for your needs can help ensure the optimal performance and longevity of your electronic systems.

Disclaimer: The views and opinions expressed by individual authors or forum participants on this website do not represent the views and opinions of Chipsmall, nor do they represent Chipsmall's official policy.

share this blog to:

