OUTLINE:
What is the difference between quantum chips and ordinary chips?
 327
327From the appearance, it is not difficult to see that quantum chips and traditional chips have a big difference in size. Besides that, do you want to know what other differences they have?
Ordinary chips, also known as classical chips, are based on the principles of classical physics and use binary digits, or bits, that can either be 0 or 1 to represent and process information. These bits are processed using electronic switches called transistors, which are arranged in circuits on a semiconductor material such as silicon.
Quantum chips, on the other hand, are based on the principles of quantum mechanics and use quantum bits, or qubits, to represent and process information. Qubits can be in multiple states simultaneously, which allows quantum chips to perform certain calculations much faster than classical chips. Quantum chips also rely on different physical systems to implement qubits, such as superconducting circuits or trapped ions.

Quantum chips are fundamentally different from ordinary chips in terms of their underlying principles, technologies, and materials.
While classical chips use binary digits and transistors on silicon-based materials, quantum chips use qubits and quantum circuits on carbon-based materials or other systems such as superconducting circuits or trapped ions.
Quantum chips have the potential to perform certain calculations much faster than classical chips, but they require specialized error correction techniques to mitigate errors. There are currently two main routes for quantum computing: solid-state devices and optical devices. Semiconductor quantum chips and superconducting quantum chips are both promising candidates for large-scale practical quantum computing in the future. Quantum computing is a cutting-edge technology field that major countries around the world are vying to lay out in recent years, relying on the imagination of computing power.
The working mechanism of qubits is different from that of classical bits, so quantum chips can handle problems that ordinary chips cannot, such as quantum computing, quantum simulation, and quantum communication.
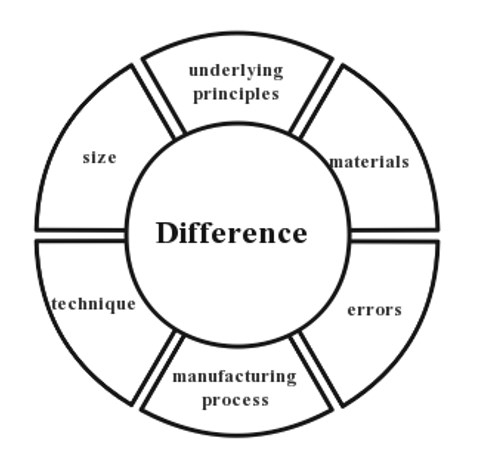
Another key difference between quantum chips and classical chips is the way they handle errors. In classical chips, errors can be corrected by adding redundancy or using error-correcting codes. However, in quantum chips, errors are much more common due to the fragile nature of qubits and the effects of decoherence. As a result, quantum chips require specialized error correction techniques and algorithms to mitigate these errors.
In addition, the manufacturing process of quantum chips is also different from that of ordinary chips. The manufacturing of quantum chips needs to be carried out at extremely low temperatures, usually below several tens of millikelvin, to avoid the influence of quantum noise.
Overall, quantum chips and classical chips are fundamentally different in their underlying principles and technologies, and each has its own strengths and limitations. While classical chips are well-suited for many everyday computing tasks, quantum chips have the potential to revolutionize fields such as cryptography, drug discovery, and optimization problems.

Disclaimer: The views and opinions expressed by individual authors or forum participants on this website do not represent the views and opinions of Chipsmall, nor do they represent Chipsmall's official policy.

share this blog to:

