OUTLINE:
Beyond Simple Switching: Exploring the World of Automotive Relays
 97
97In the complex world of automobiles, automotive relays play a vital role in managing your car's electrical system. They leverage electromagnetism to control high currents with low currents, protecting circuits and ensuring proper functioning of various electrical components in your car.
What Is Automotive Relays
Automotive relays play a vital role in managing your car's electrical system. They act like electronically controlled switches, essentially working behind the scenes to ensure various electrical components function properly.

Function : An automotive relay is an electromechanical device that uses a small electrical current to control a much larger electrical current. It essentially acts like a switch, but instead of being flipped manually, it's activated by an electrical signal.
Applications of Automotive Relays:
-
Headlights: Relays ensure headlights receive full power without overloading the headlight switch.
-
Fuel Pumps: Relays can activate the fuel pump only when the engine is cranking or running.
-
Electric Fans: Relays can control electric cooling fans based on engine temperature.
-
Window Motors: Relays can provide the high current needed for powerful window motors.
-
Audio Systems: Relays can manage power flow to amplifiers and other audio components.
Working Principle of Automotive Relays
Automotive Relays allow a small electrical current to control a much larger current, ensuring various electrical components function properly. Here's a breakdown of their working principle:
Components
-
Electromagnet (Coil):A coil of wire that creates a magnetic field when an electric current flows through it.
Contacts:A set of metal contacts that act like a switch, opening or closing a circuit. They typically come in two configurations: Normally Open (NO) and Normally Closed (NC).
Spring:A spring that holds the contacts in their default position (usually Normally Open) until the electromagnet is activated.
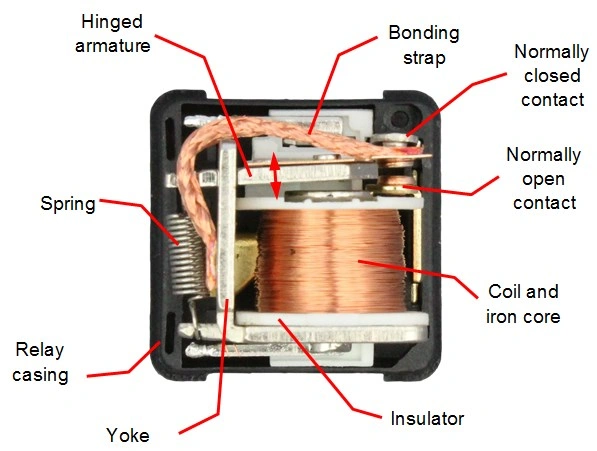
Image Source: 12 Volt Planet
Working Principle
-
Activation Signal: When you turn on a car component like headlights (represented by the switch in the diagram below), it sends a small electrical current to the relay's coil.
-
Electromagnetic Effect: The current flowing through the coil creates a magnetic field.
-
Contact Activation: This magnetic field attracts a lever or armature within the relay, causing it to move. The spring usually holds the armature in a position where the Normally Open (NO) contacts are separated.
-
Circuit Control: With the armature pulled by the magnet, the Normally Open (NO) contacts touch, completing a circuit and allowing a larger current to flow to the car component (headlights in this example). The Normally Closed (NC) contacts, if present, will open (depending on the relay design) to interrupt a different circuit.
Maintenance of Automotive Relay
Automotive relays are generally reliable components and don't require frequent maintenance. However, with time and wear, they can malfunction. So following are some ways to keep them in good condition:
General Maintenance Tips:
-
Visual Inspection: During routine maintenance checks, visually inspect relays for any signs of damage like corrosion on the housing or loose connections on the terminals.
-
Listen for Clicking: When you activate a relay-controlled component (like headlights), listen for a clicking sound. This clicking indicates the relay is functioning and switching the contacts. The absence of a click could suggest a faulty relay.
-
Consult your Car's Manual: Your car's manual will likely have a section on fuse and relay locations. Refer to it to identify specific relays and any recommended maintenance procedures.
Troubleshooting and Replacement:
-
Identify the Problem: If you suspect a relay is malfunctioning, research the symptoms related to that specific relay in your car (e.g., headlights not turning on, fan not running). This can help narrow down the culprit.
-
Testing (if possible): Some relays might be easily accessible and allow for basic testing using a multimeter to check for continuity across contacts. However, consult a qualified mechanic if unsure about the testing procedure.
-
Replacement: If a relay is confirmed faulty, it's best to replace it with a high-quality, OEM-compatible (Original Equipment Manufacturer) part. Here's a general process for relay replacement:
-
Turn off and disconnect the battery: Safety first! Always disconnect the battery before working on any electrical components in your car.
-
Locate the relay: Refer to your car's manual for the specific location and removal procedure for the relay you're replacing.
-
Remove the faulty relay: Once located, carefully remove the old relay by following the recommended method (e.g., unplugging a connector or removing retaining clips).
-
Install the new relay: Make sure the new relay matches the specifications and pin configuration of the old one. Gently insert the new relay into its designated socket.
-
Reconnect the battery and test: Reconnect the battery and test the car component controlled by the relay to ensure it functions properly.
-
Conclusion
In essence, automotive relays are like silent conductors in your car's electrical orchestra. They efficiently manage power flow, protect delicate circuits, and ensure various components function as intended, keeping your car running smoothly and safely.

Disclaimer: The views and opinions expressed by individual authors or forum participants on this website do not represent the views and opinions of Chipsmall, nor do they represent Chipsmall's official policy.

share this blog to:











